Page 253 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 253
Sec. 5.1 Batch Reactor Data 225
-
"
k,= - (dm3/mol)a+P-1/s
=
c:c;
Both a and p can be determined by using the method of excess, coupled with
a differential analysis of data for batch systems.
To outline the procedure used in the differential method of analysis, we
consider a reaction carried out isothermally in a constant-volume batch reactor
and the concentration recorded as a function of time. By combining the mole
balance with the rate law given by Equation (5-l), we obtain
Constant-volume
batch reactor (5-6)
After taking the natural logarithm of both sides of.Equation (5-61,
I I
observe that the slope of a plot of In( -dC,ldt) as a function of (InC,) is the
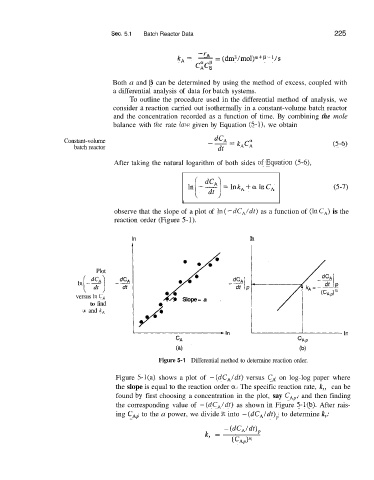
reaction order (Figure 5-1).
In In
/
Plot
versus In CA e. e. = a
Slope
to find
(Y and k,
Figure 5-1 Differential method to determine reaction order.
Figure S-l(a) shows a plot of - (dC,/dt) versus CA on log-log paper where
the slope is equal to the reaction order a. The specific reaction rate, k,, can be
found by first choosing a concentration in the plot, say C,,, and then finding
the corresponding value of - (dCA/dt) as shown in Figure 5-l(b). After rais-
ing CAI, to the a power, we divide it into - (dC,/dt), to determine k,:
- (dC,/dt),
k, =
( CAp)a