Page 399 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering Ebook
P. 399
370 Nonelementary Reaction Kinetics Chap. 7
L i
where 2 P, is the total dead polymer concentration and
(7-27)
which is the same as the mole fraction obtained in step polymerization, i.e.
Equation (7-27).
h If the termination is only by disproportionation, the dead polymer PI will
Live have the same distribution as the live polymer RI.
We will discuss the use of the Flory Equation after we discuss molecular
weight distributions.
7.3.4 Molecular Weight Distribution
Although it is of interest to know the monomer concentration as a func-
tion of time (Figure 7-5), it is the polymer concentration, the average molecu-
lar weight, and the distribution of chain lengths that give a polymer its unique
properties. Consequently, to obtain such things as the average chain length of
the polymer, we need to determine the molecular weight distribution of radi-
cals, (live polymer) R,, and then dead polymers P, as well as the molecular
weight distribution. Consequently, we need to quantify these parameters. A
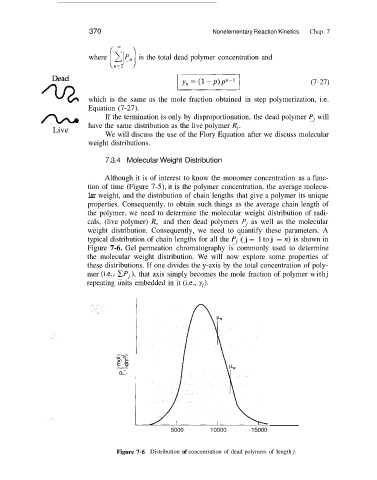
typical distribution of chain lengths for all the PI (j = 1 to j = n) is shown in
Figure 7-6. Gel permeation chromatography is commonly used to determine
the molecular weight distribution. We will now explore some properties of
these distributions. If one divides the y-axis by the total concentration of poly-
mer (i.e., CP,), that axis simply becomes the mole fraction of polymer withj
repeating units embedded in it (Le., yI).
-
-D
El &
-
a-
5000 10000 15000
Figure 7-6 Distribution of concentration of dead polymers of length j.