Page 50 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering Ebook
P. 50
Sec. 1 .!5 Industrial Reactors 21
Flue gas
t
Product gas
/A * Products
1
Reactor
/Steam
Naphtha and
recycle gas
I
Feed gas Compressed air 2 Furnace
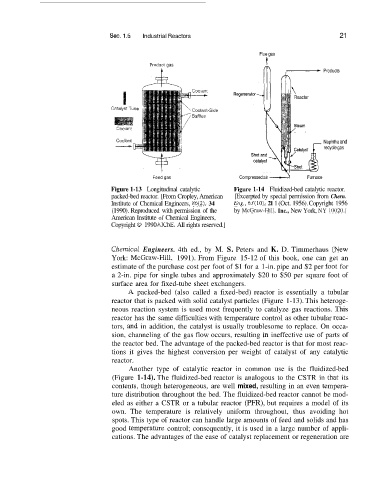
Figure 1-13 Longitudinal catalytic Figure 1-14 Fluidized-bed catalytic reactor.
packed-bed reactor. [From Cropley, American [Excerpted by special permission from Chern.
Institute of Chemical Engineers, 86(2), 34 Eng., 63(10), 21 1 (Oct. 1956). Copyright 1956
(1990). Reproduced with permission of the by McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York, NY 10020.1
American Institute of Chemical Engineers,
Copyright 0 1990 PiIChE. All rights reserved.]
ChemicaE Engineers. 4th ed., by M. S. Peters and K. D. Timmerhaus (New
York: McGraw-Hill, 1991). From Figure 15-12 of this book, one can get an
estimate of the purchase cost per foot of $1 for a 1-in. pipe and $2 per foot for
a 2-in. pipe for single tubes and approximately $20 to $50 per square foot of
surface area for fixed-tube sheet exchangers.
A packed-bed (also called a fixed-bed) reactor is essentially a tubular
reactor that is packed with solid catalyst particles (Figure 1-13). This heteroge-
neous reaction system is used most frequently to catalyze gas reactions. This
reactor has the same difficulties with temperature control as other tubular rleac-
tors, and in addition, the catalyst is usually troublesome to replace. On occa-
sion, channeling of the gas flow occurs, resulting in ineffective use of parts of
the reactor bed. The advantage of the packed-bed reactor is that for most reac-
tions it gives the highest conversion per weight of catalyst of any catalytic
reactor.
Another type of catalytic reactor in common use is the fluidized-bed
(Figure 1-14). The fluidized-bed reactor is analogous to the CSTR in thait its
contents, though heterogeneous, are well mixed, resulting in an even tempera-
ture distribution throughout the bed. The fluidized-bed reactor cannot be mod-
eled as either a CSTR or a tubular reactor (PFR), but requires a model of its
own. The temperature is relatively uniform throughout, thus avoiding hot
spots. This type of reactor can handle large amounts of feed and solids and has
good temperaturie control; consequently, it is used in a large number of appli-
cations. The advantages of the ease of catalyst replacement or regeneration are