Page 281 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 281
Other Platforms for Embedded Systems
PC/104 Bus
The PC/104 bus compresses the PC architecture to a form factor better suited to
small embedded systems. The PC/104 bus is almost electrically identical to the ISA
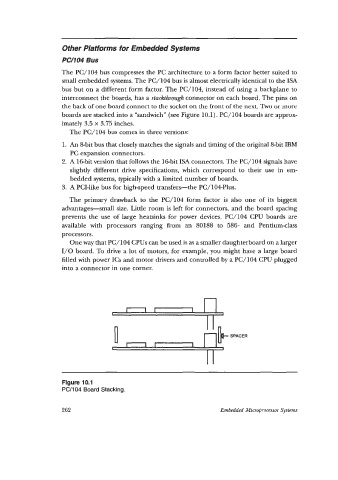
bus but on a different form factor. The PC/104, instead of using a backplane to
interconnect the boards, has a stackthrough connector on each board. The pins on
the back of one board connect to the socket on the front of the next. Two or more
boards are stacked into a “sandwich” (see Figure 10.1). PC/104 boards are approx-
imately 3.5 x 3.75 inches.
The PC/104 bus comes in three versions:
1. An &bit bus that closely matches the signals and timing of the original 8-bit IBM
PC expansion connectors.
2. A 16-bit version that follows the 16-bit ISA connectors. The PC/104 signals have
slightly different drive specifications, which correspond to their use in em-
bedded systems, typically with a limited number of boards.
3. A PCI-like bus for high-speed transfers-the PC/lO4Plus.
The primary drawback to the PC/104 form factor is also one of its biggest
advantages-small size. Little room is left for connectors, and the board spacing
prevents the use of large heatsinks for power devices. PC/104 CPU boards are
available with processors ranging from an 80188 to 586- and Pentiumclass
processors.
One way that PC/104 CPUs can be used is as a smaller daughterboard on a larger
1/0 board. To drive a lot of motors, for example, you might have a large board
filled with power ICs and motor drivers and controlled by a PC/104 CPU plugged
into a connector in one corner.
Figure 10.1
PC/104 Board Stacking.
262 Embedded Microprocessm Systems