Page 660 - Encyclopedia of Business and Finance
P. 660
eobf_R 7/5/06 3:20 PM Page 637
Records Management
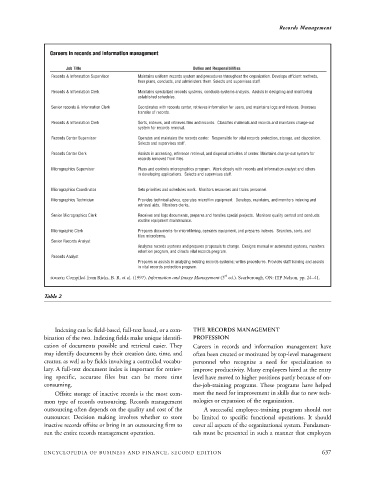
Careers in records and information management
Job Title Duties and Responsibilities
Records & Information Supervisor Maintains uniform records system and procedures throughout the organization. Develops efficient methods,
then plans, conducts, and administers them. Selects and supervises staff.
Records & Information Clerk Maintains specialized records systems, conducts systems analysis. Assists in designing and monitoring
established schedules.
Senior records & Information Clerk Coordinates with records center, retrieves information for users, and maintains logs and indexes. Oversees
transfer of records.
Records & Information Clerk Sorts, indexes, and retrieves files and records. Classifies materials and records and maintains charge-out
system for records removal.
Records Center Supervisor Operates and maintains the records center. Responsible for vital records protection, storage, and disposition.
Selects and supervises staff.
Records Center Clerk Assists in accessing, reference retrieval, and disposal activities of center. Maintains charge-out system for
records removed from files.
Micrographics Supervisor Plans and controls micrographics program. Work closely with records and information analyst and others
in developing applications. Selects and supervises staff.
Micrographics Coordinator Sets priorities and schedules work. Monitors resources and trains personnel.
Micrographics Technician Provides technical advice, operates microfilm equipment. Develops, maintains, and monitors indexing and
retrieval aids. Monitors clerks.
Senior Micrographics Clerk Receives and logs documents, prepares and handles special projects. Monitors quality control and conducts
routine equipment maintenance.
Micrographic Clerk Prepares documents for microfilming, operates equipment, and prepares indexes. Searches, sorts, and
files microforms.
Senior Records Analyst
Analyzes records systems and prepares proposals to change. Designs manual or automated systems, monitors
retention program, and directs vital records program.
Records Analyst
Prepares or assists in analyzing existing records systems; writes procedures. Provides staff training and assists
in vital records protection program.
rd
SOURCE: Compiled from Ricks, B. R. et al. (1997). Information and Image Management (3 ed.). Scarborough, ON: ITP Nelson, pp. 24–41.
Table 2
Indexing can be field-based, full-text based, or a com- THE RECORDS MANAGEMENT
bination of the two. Indexing fields make unique identifi- PROFESSION
cation of documents possible and retrieval easier. They Careers in records and information management have
may identify documents by their creation date, time, and often been created or motivated by top-level management
creator, as well as by fields involving a controlled vocabu- personnel who recognize a need for specialization to
lary. A full-text document index is important for retriev- improve productivity. Many employees hired at the entry
ing specific, accurate files but can be more time level have moved to higher positions partly because of on-
consuming. the-job-training programs. These programs have helped
Offsite storage of inactive records is the most com- meet the need for improvement in skills due to new tech-
mon type of records outsourcing. Records management nologies or expansion of the organization.
outsourcing often depends on the quality and cost of the A successful employee-training program should not
outsourcer. Decision making involves whether to store be limited to specific functional operations. It should
inactive records offsite or bring in an outsourcing firm to cover all aspects of the organizational system. Fundamen-
run the entire records management operation. tals must be presented in such a manner that employers
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF BUSINESS AND FINANCE, SECOND EDITION 637