Page 664 - Encyclopedia of Business and Finance
P. 664
eobf_R 7/5/06 3:20 PM Page 641
Research in Business
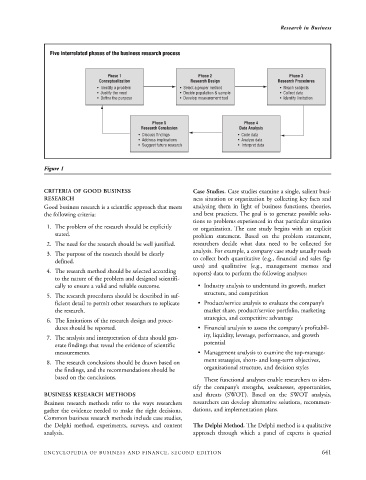
Five interrelated phases of the business research process
Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3
Conceptualization Research Design Research Procedures
• Identify a problem • Select a proper method • Reach subjects
• Justify the need • Decide population & sample • Collect data
• Define the purpose • Develop measurement tool • Identify limitation
Phase 5 Phase 4
Research Conslusion Data Analysis
• Discuss findings • Code data
• Address implications • Analyze data
• Suggest future research • Interpret data
Figure 1
CRITERIA OF GOOD BUSINESS Case Studies. Case studies examine a single, salient busi-
RESEARCH ness situation or organization by collecting key facts and
Good business research is a scientific approach that meets analyzing them in light of business functions, theories,
the following criteria: and best practices. The goal is to generate possible solu-
tions to problems experienced in that particular situation
1. The problem of the research should be explicitly or organization. The case study begins with an explicit
stated. problem statement. Based on the problem statement,
2. The need for the research should be well justified. researchers decide what data need to be collected for
analysis. For example, a company case study usually needs
3. The purpose of the research should be clearly
to collect both quantitative (e.g., financial and sales fig-
defined.
ures) and qualitative (e.g., management memos and
4. The research method should be selected according
reports) data to perform the following analyses:
to the nature of the problem and designed scientifi-
cally to ensure a valid and reliable outcome. • Industry analysis to understand its growth, market
structure, and competition
5. The research procedures should be described in suf-
ficient detail to permit other researchers to replicate • Product/service analysis to evaluate the company’s
the research. market share, product/service portfolio, marketing
strategies, and competitive advantage
6. The limitations of the research design and proce-
dures should be reported. • Financial analysis to assess the company’s profitabil-
ity, liquidity, leverage, performance, and growth
7. The analysis and interpretation of data should gen-
potential
erate findings that reveal the evidence of scientific
measurements. • Management analysis to examine the top-manage-
ment strategies, short- and long-term objectives,
8. The research conclusions should be drawn based on
organizational structure, and decision styles
the findings, and the recommendations should be
based on the conclusions. These functional analyses enable researchers to iden-
tify the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities,
BUSINESS RESEARCH METHODS and threats (SWOT). Based on the SWOT analysis,
Business research methods refer to the ways researchers researchers can develop alternative solutions, recommen-
gather the evidence needed to make the right decisions. dations, and implementation plans.
Common business research methods include case studies,
the Delphi method, experiments, surveys, and content The Delphi Method. The Delphi method is a qualitative
analysis. approach through which a panel of experts is queried
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF BUSINESS AND FINANCE, SECOND EDITION 641