Page 104 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 104
O - O
S
O - O O
O O
K + S Al 3+
- O O
OTHER NAMES:
See Overview.
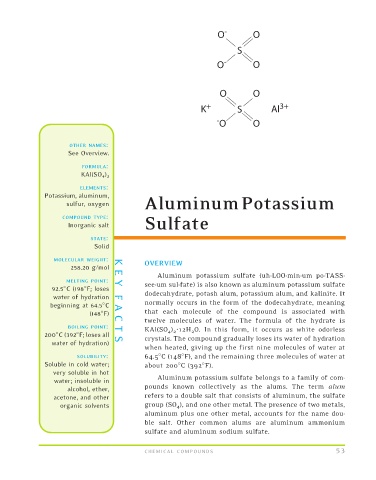
FORMULA:
KAl(SO 4 ) 2
ELEMENTS:
Potassium, aluminum,
AluminumPotassium
sulfur, oxygen
COMPOUND TYPE:
Inorganic salt Sulfate
STATE:
Solid
MOLECULAR WEIGHT:
OVERVIEW
258.20 g/mol KE
Aluminum potassium sulfate (uh-LOO-min-um po-TASS-
MELTING POINT:
Y see-um sul-fate) is also known as aluminum potassium sulfate
92.5 C (198 F; loses
dodecahydrate, potash alum, potassium alum, and kalinite. It
water of hydration F
normally occurs in the form of the dodecahydrate, meaning
beginning at 64.5 C
that each molecule of the compound is associated with
A
twelve molecules of water. The formula of the hydrate is
(148 F) C
BOILING POINT:
T KAl(SO 4 ) 2 12H 2 O. In this form, it occurs as white odorless
crystals. The compound gradually loses its water of hydration
water of hydration)
200 C (392 F; loses all S
when heated, giving up the first nine molecules of water at
SOLUBILITY: 64.5 C (148 F), and the remaining three molecules of water at
Soluble in cold water; about 200 C (392 F).
very soluble in hot
Aluminum potassium sulfate belongs to a family of com-
water; insoluble in
pounds known collectively as the alums. The term alum
alcohol, ether,
acetone, and other refers to a double salt that consists of aluminum, the sulfate
organic solvents group (SO 4 ), and one other metal. The presence of two metals,
aluminum plus one other metal, accounts for the name dou-
ble salt. Other common alums are aluminum ammonium
sulfate and aluminum sodium sulfate.
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 53