Page 124 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 124
H O
+ -
N N
H H
H O O
OTHER NAMES:
German saltpeter;
Norway saltpeter;
nitric acid,
ammonium salt
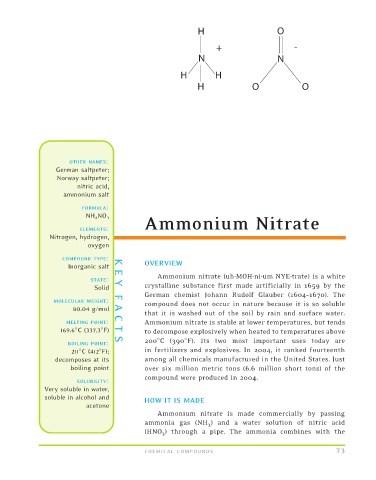
FORMULA:
NH 4 NO 3
Ammonium Nitrate
ELEMENTS:
Nitrogen, hydrogen,
oxygen
COMPOUND TYPE:
OVERVIEW
Inorganic salt KE
Ammonium nitrate (uh-MOH-ni-um NYE-trate) is a white
STATE: Y
Solid crystalline substance first made artificially in 1659 by the
German chemist Johann Rudolf Glauber (1604–1670). The
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: F
compound does not occur in nature because it is so soluble
80.04 g/mol A
that it is washed out of the soil by rain and surface water.
MELTING POINT: C Ammonium nitrate is stable at lower temperatures, but tends
169.6 C (337.3 F) T to decompose explosively when heated to temperatures above
BOILING POINT: 200 C (390 F). Its two most important uses today are
S
211 C (412 F); in fertilizers and explosives. In 2004, it ranked fourteenth
decomposes at its among all chemicals manufactured in the United States. Just
boiling point over six million metric tons (6.6 million short tons) of the
compound were produced in 2004.
SOLUBILITY:
Very soluble in water,
soluble in alcohol and
HOW IT IS MADE
acetone
Ammonium nitrate is made commercially by passing
ammonia gas (NH 3 ) and a water solution of nitric acid
(HNO 3 ) through a pipe. The ammonia combines with the
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 73