Page 128 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 128
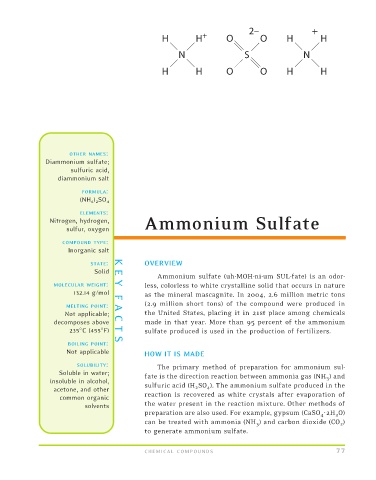
2– +
H H + O O H H
N S N
H H O O H H
OTHER NAMES:
Diammonium sulfate;
sulfuric acid,
diammonium salt
FORMULA:
(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4
ELEMENTS:
Nitrogen, hydrogen, Ammonium Sulfate
sulfur, oxygen
COMPOUND TYPE:
Inorganic salt
STATE: KE OVERVIEW
Solid
Ammonium sulfate (uh-MOH-ni-um SUL-fate) is an odor-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: Y less, colorless to white crystalline solid that occurs in nature
as the mineral mascagnite. In 2004, 2.6 million metric tons
132.14 g/mol F
MELTING POINT: A (2.9 million short tons) of the compound were produced in
the United States, placing it in 21st place among chemicals
made in that year. More than 95 percent of the ammonium
Not applicable; C
235 C (455 F) sulfate produced is used in the production of fertilizers.
decomposes above T
BOILING POINT: S
Not applicable
HOW IT IS MADE
SOLUBILITY: The primary method of preparation for ammonium sul-
Soluble in water;
fate is the direction reaction between ammonia gas (NH 3 ) and
insoluble in alcohol,
sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ). The ammonium sulfate produced in the
acetone, and other
reaction is recovered as white crystals after evaporation of
common organic
solvents the water present in the reaction mixture. Other methods of
preparation are also used. For example, gypsum (CaSO 4 2H 2 O)
can be treated with ammonia (NH 3 ) and carbon dioxide (CO 2 )
to generate ammonium sulfate.
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 77