Page 180 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 180
H H
H
C C
H C C S
3
H H H
H
OTHER NAMES:
Three forms of butyl
mercaptan exist; see
Overview
FORMULA:
C 4 H 10 S
ELEMENTS:
Carbon, hydrogen Butyl Mercaptan
sulfur
COMPOUND TYPE:
Mercaptan (organic)
STATE: OVERVIEW
Liquid KE
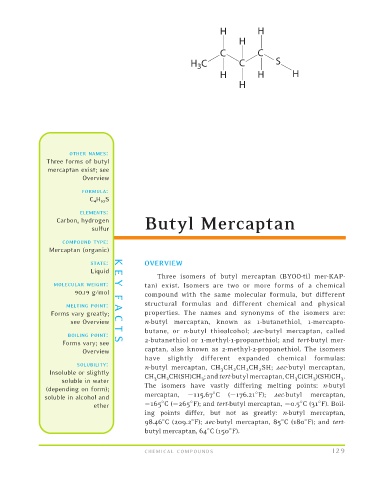
Three isomers of butyl mercaptan (BYOO-til mer-KAP-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: Y tan) exist. Isomers are two or more forms of a chemical
compound with the same molecular formula, but different
90.19 g/mol F
MELTING POINT: A structural formulas and different chemical and physical
properties. The names and synonyms of the isomers are:
see Overview n-butyl mercaptan, known as 1-butanethiol, 1-mercapto-
Forms vary greatly; C
butane, or n-butyl thioalcohol; sec-butyl mercaptan, called
T
2-butanethiol or 1-methyl-1-propanethiol; and tert-butyl mer-
Forms vary; see
BOILING POINT: S
captan, also known as 2-methyl-2-propanethiol. The isomers
Overview
have slightly different expanded chemical formulas:
SOLUBILITY:
n-butyl mercaptan, CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 SH; sec-butyl mercaptan,
Insoluble or slightly
CH 3 CH 2 CH(SH)CH 3 ;andtert-butylmercaptan,CH 3 C(CH 3 )(SH)CH 3 .
soluble in water
The isomers have vastly differing melting points: n-butyl
(depending on form);
mercaptan, 115.67 C ( 176.21 F); sec-butyl mercaptan,
soluble in alcohol and
ether 165 C( 265 F); and tert-butyl mercaptan, 0.5 C(31 F). Boil-
ing points differ, but not as greatly: n-butyl mercaptan,
98.46 C(209.2 F); sec-butyl mercaptan, 85 C(180 F); and tert-
butyl mercaptan, 64 C(150 F).
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 129