Page 206 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 206
O
3 –
O P O Ca 2+
O Ca 2+
O
3 –
O P O
Ca 2+
O
OTHER NAMES:
see Overview
Calcium Phosphate
FORMULA:
see Overview
ELEMENTS:
calcium, hydrogen,
phosphorus, oxygen KE OVERVIEW
COMPOUND TYPE: The three forms of calcium phosphate (KAL-see-um FOSS-
Inorganic salts Y fate) all occur as tasteless, odorless, colorless to white crystalline
STATE: F or powdery solids.
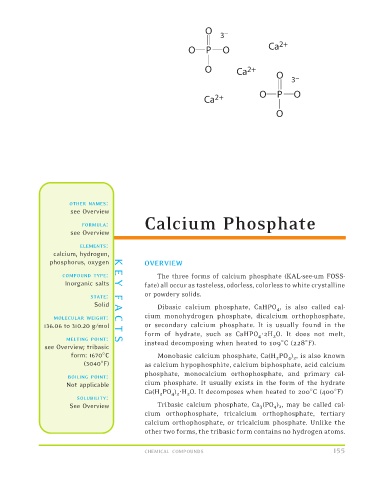
Solid A Dibasic calcium phosphate, CaHPO 4 , is also called cal-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: C cium monohydrogen phosphate, dicalcium orthophosphate,
136.06 to 310.20 g/mol T or secondary calcium phosphate. It is usually found in the
form of hydrate, such as CaHPO 4 2H 2 O. It does not melt,
MELTING POINT: S
instead decomposing when heated to 109 C (228 F).
see Overview; tribasic
form: 1670 C Monobasic calcium phosphate, Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 , is also known
(3040 F) as calcium hypophosphite, calcium biphosphate, acid calcium
phosphate, monocalcium orthophosphate, and primary cal-
BOILING POINT:
Not applicable cium phosphate. It usually exists in the form of the hydrate
Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 H 2 O. It decomposes when heated to 200 C(400 F)
SOLUBILITY:
See Overview Tribasic calcium phosphate, Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 , may be called cal-
cium orthophosphate, tricalcium orthophosphate, tertiary
calcium orthophosphate, or tricalcium phosphate. Unlike the
other two forms, the tribasic form contains no hydrogen atoms.
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 155