Page 126 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 126
P1: GLQ/GUB P2: FYK Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007K-319 July 2, 2001 17:53
436 Hybridomas, Genetic Engineering of
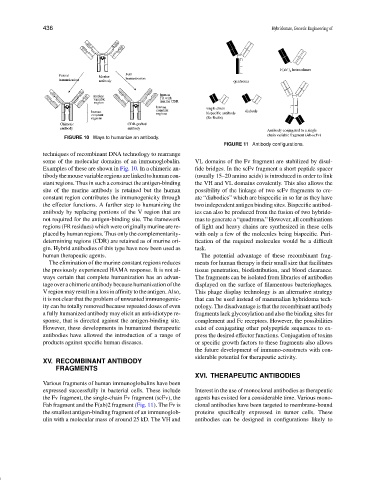
FIGURE 10 Ways to humanize an antibody.
FIGURE 11 Antibody configurations.
techniques of recombinant DNA technology to rearrange
some of the molecular domains of an immunoglobulin. VL domains of the Fv fragment are stabilized by disul-
Examples of these are shown in Fig. 10. In a chimeric an- fide bridges. In the scFv fragment a short peptide spacer
tibodythemousevariableregionsarelinkedtohumancon- (usually 15–20 amino acids) is introduced in order to link
stant regions. Thus in such a construct the antigen-binding the VH and VL domains covalently. This also allows the
site of the murine antibody is retained but the human possibility of the linkage of two scFv fragments to cre-
constant region contributes the immunogenicity through ate “diabodies” which are bispecificinsofarastheyhave
the effector functions. A further step to humanizing the two independent antigen binding sites. Bispecific antibod-
antibody by replacing portions of the V region that are ies can also be produced from the fusion of two hybrido-
not required for the antigen-binding site. The framework mas to generate a “quadroma.” However, all combinations
regions (FR residues) which were originally murine are re- of light and heavy chains are synthesized in these cells
placed by human regions. Thus only the complementarity- with only a few of the molecules being bispecific. Puri-
determining regions (CDR) are retained as of murine ori- fication of the required molecules would be a difficult
gin. Hybrid antibodies of this type have now been used as task.
human therapeutic agents. The potential advantage of these recombinant frag-
The elimination of the murine constant regions reduces ments for human therapy is their small size that facilitates
the previously experienced HAMA response. It is not al- tissue penetration, biodistribution, and blood clearance.
ways certain that complete humanization has an advan- The fragments can be isolated from libraries of antibodies
tage over a chimeric antibody because humanization of the displayed on the surface of filamentous bacteriophages.
V region may result in a loss in affinity to the antigen. Also, This phage display technology is an alternative strategy
it is not clear that the problem of unwanted immunogenic- that can be used instead of mammalian hybridoma tech-
ity can be totally removed because repeated doses of even nology. The disadvantage is that the recombinant antibody
a fully humanized antibody may elicit an anti-idiotype re- fragments lack glycosylation and also the binding sites for
sponse, that is directed against the antigen-binding site. complement and Fc receptors. However, the possibilities
However, these developments in humanized therapeutic exist of conjugating other polypeptide sequences to ex-
antibodies have allowed the introduction of a range of press the desired effector functions. Conjugation of toxins
products against specific human diseases. or specific growth factors to these fragments also allows
the future development of immuno-constructs with con-
siderable potential for therapeutic activity.
XV. RECOMBINANT ANTIBODY
FRAGMENTS
XVI. THERAPEUTIC ANTIBODIES
Various fragments of human immunoglobulins have been
expressed successfully in bacterial cells. These include Interest in the use of monoclonal antibodies as therapeutic
the Fv fragment, the single-chain Fv fragment (scFv), the agents has existed for a considerable time. Various mono-
Fab fragment and the F(ab)2 fragment (Fig. 11). The Fv is clonal antibodies have been targeted to membrane-bound
the smallest antigen-binding fragment of an immunoglob- proteins specifically expressed in tumor cells. These
ulin with a molecular mass of around 25 kD. The VH and antibodies can be designed in configurations likely to