Page 210 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 210
P1: GTV/MBR P2: GSS Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN011L-523 August 10, 2001 11:17
330 Optical Fiber Techniques for Medical Applications
an artery in the leg and guided into the left ventricle. The
distal tip of the fiber is brought in contact with the inner
side of the myocardium. Short laser pulses are used to
drill channels, roughly halfway through the myocardium
wall. Clinical investigations, using various lasers, are in
progress in several medical centers.
3. Closed Chest Endoscopic Surgery
on a Beating Heart
Cardiac surgeons would like to replace the open-heart
CABG surgery with a closed chest, minimally inva-
sive, bypass operation. Recent advancements have been
achieved with the help of the robotic surgery, using a sys-
tem similar to the one described in Section VI.D. This
computer controlled robotic system provides the exquisite
accuracy needed for the bypass coronary surgery. The ar-
ticulated arms of the robot, equipped with surgical tools,
are used to perform the whole endoscopic CABG opera-
tion on a beating heart, without arresting the operation of
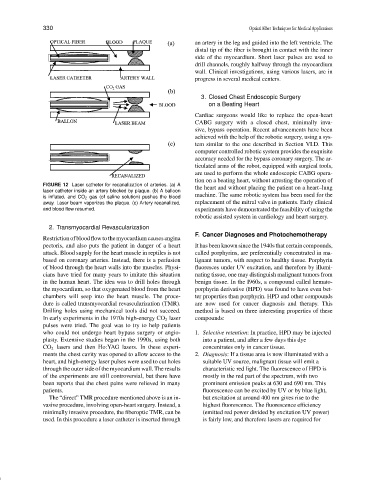
FIGURE 12 Laser catheter for recanalization of arteries. (a) A
the heart and without placing the patient on a heart–lung
laser catheter inside an artery blocked by plaque. (b) A balloon
machine. The same robotic system has been used for the
is inflated, and CO 2 gas (of saline solution) pushes the blood
away. Laser beam vaporizes the plaque. (c) Artery recanalized, replacement of the mitral valve in patients. Early clinical
and blood flow resumed. experiments have demonstrated the feasibility of using the
robotic assisted system in cardiology and heart surgery.
2. Transmyocardial Revascularization
F. Cancer Diagnoses and Photochemotherapy
Restriction of blood flow to the myocardium causes angina
pectoris, and also puts the patient in danger of a heart It has been known since the 1940s that certain compounds,
attack. Blood supply for the heart muscle in reptiles is not called porphyrins, are preferentially concentrated in ma-
based on coronary arteries. Instead, there is a perfusion lignant tumors, with respect to healthy tissue. Porphyrin
of blood through the heart walls into the muscles. Physi- fluoresces under UV excitation, and therefore by illumi-
cians have tried for many years to imitate this situation nating tissue, one may distinguish malignant tumors from
in the human heart. The idea was to drill holes through benign tissue. In the I960s, a compound called hemato-
the myocardium, so that oxygenated blood from the heart porphyrin derivative (HPD) was found to have even bet-
chambers will seep into the heart muscle. The proce- ter properties than porphyrin. HPD and other compounds
dure is called transmyocardial revascularization (TMR). are now used for cancer diagnosis and therapy. This
Drilling holes using mechanical tools did not succeed. method is based on three interesting properties of these
In early experiments in the 1970s high-energy CO 2 laser compounds:
pulses were tried. The goal was to try to help patients
who could not undergo heart bypass surgery or angio- 1. Selective retention: In practice, HPD may be injected
plasty. Extensive studies began in the 1990s, using both into a patient, and after a few days this dye
CO 2 lasers and then Ho:YAG lasers. In these experi- concentrates only in cancer tissue.
ments the chest cavity was opened to allow access to the 2. Diagnosis: If a tissue area is now illuminated with a
heart, and high-energy laser pulses were used to cut holes suitable UV source, malignant tissue will emit a
through the outer side of the myocardium wall. The results characteristic red light. The fluorescence of HPD is
of the experiments are still controversial, but there have mostly in the red part of the spectrum, with two
been reports that the chest pains were relieved in many prominent emission peaks at 630 and 690 nm. This
patients. fluorescence can be excited by UV or by blue light,
The “direct” TMR procedure mentioned above is an in- but excitation at around 400 nm gives rise to the
vasive procedure, involving open-heart surgery. Instead, a highest fluorescence. The fluorescence efficiency
minimally invasive procedure, the fiberoptic TMR, can be (emitted red power divided by excitation UV power)
used. In this procedure a laser catheter is inserted through is fairly low, and therefore lasers are required for