Page 365 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 365
P1: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009K-419 July 19, 2001 20:57
300 Membranes, Synthetic, Applications
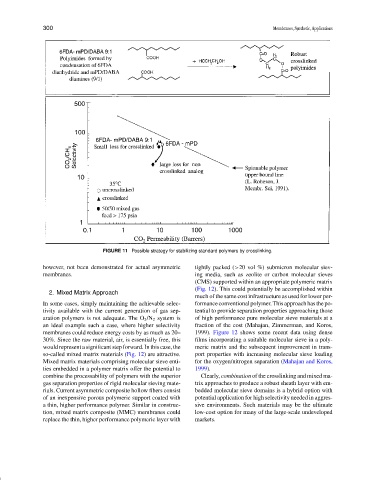
FIGURE 11 Possible strategy for stabilizing standard polymers by crosslinking.
however, not been demonstrated for actual asymmetric tightly packed (>20 vol %) submicron molecular siev-
membranes. ing media, such as zeolite or carbon molecular sieves
(CMS) supported within an appropriate polymeric matrix
(Fig. 12). This could potentially be accomplished within
2. Mixed Matrix Approach
much of the same cost infrastructure as used for lower per-
In some cases, simply maintaining the achievable selec- formance conventional polymer. This approach has the po-
tivity available with the current generation of gas sep- tential to provide separation properties approaching those
aration polymers is not adequate. The O 2 /N 2 system is of high performance pure molecular sieve materials at a
an ideal example such a case, where higher selectivity fraction of the cost (Mahajan, Zimmerman, and Koros,
membranes could reduce energy costs by as much as 20– 1999). Figure 12 shows some recent data using dense
30%. Since the raw material, air, is essentially free, this films incorporating a suitable molecular sieve in a poly-
would represent a significant step forward. In this case, the meric matrix and the subsequent improvement in trans-
so-called mixed matrix materials (Fig. 12) are attractive. port properties with increasing molecular sieve loading
Mixed matrix materials comprising molecular sieve enti- for the oxygen/nitrogen separation (Mahajan and Koros,
ties embedded in a polymer matrix offer the potential to 1999).
combine the processability of polymers with the superior Clearly, combination of the crosslinking and mixed ma-
gas separation properties of rigid molecular sieving mate- trix approaches to produce a robust sheath layer with em-
rials. Current asymmetric composite hollow fibers consist bedded molecular sieve domains is a hybrid option with
of an inexpensive porous polymeric support coated with potential application for high selectivity needed in aggres-
a thin, higher performance polymer. Similar in construc- sive environments. Such materials may be the ultimate
tion, mixed matrix composite (MMC) membranes could low-cost option for many of the large-scale undeveloped
replace the thin, higher performance polymeric layer with markets.