Page 440 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 440
P1: GLQ/GUB P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012I-591 July 26, 2001 15:54
606 Pollution Prevention from Chemical Processes
opportunities may exist during process engineering and
should be explored. The potential to reduce waste and pol-
lutant releases in this stage is impacted by the selection
of process configuration (batch versus continuous, for ex-
ample), process conditions (such as temperature and pres-
sure), manufacturing procedures, design and selection of
processing equipment, and process control schemes.
As a project moves into the detailed design stage
(sometimes referred to as the “mechanical design stage”
or “production design”), source reduction opportunities
typically diminish. The main reason is that the process
and preliminary plant design become fixed and the project
becomes schedule-driven. The focus at this stage shifts
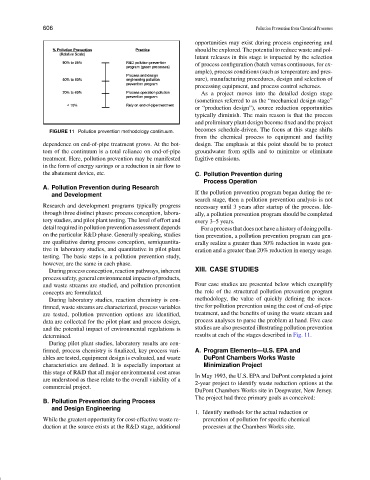
FIGURE 11 Pollution prevention methodology continuum.
from the chemical process to equipment and facility
dependence on end-of-pipe treatment grows. At the bot- design. The emphasis at this point should be to protect
tom of the continuum is a total reliance on end-of-pipe groundwater from spills and to minimize or eliminate
treatment. Here, pollution prevention may be manifested fugitive emissions.
in the form of energy savings or a reduction in air flow to
the abatement device, etc. C. Pollution Prevention during
Process Operation
A. Pollution Prevention during Research
and Development If the pollution prevention program began during the re-
search stage, then a pollution prevention analysis is not
Research and development programs typically progress necessary until 3 years after startup of the process. Ide-
through three distinct phases: process conception, labora- ally, a pollution prevention program should be completed
tory studies, and pilot plant testing. The level of effort and every 3–5 years.
detailrequiredinpollutionpreventionassessmentdepends For a process that does not have a history of doing pollu-
on the particular R&D phase. Generally speaking, studies tion prevention, a pollution prevention program can gen-
are qualitative during process conception, semiquantita- erally realize a greater than 30% reduction in waste gen-
tive in laboratory studies, and quantitative in pilot plant eration and a greater than 20% reduction in energy usage.
testing. The basic steps in a pollution prevention study,
however, are the same in each phase.
During process conception, reaction pathways, inherent XIII. CASE STUDIES
process safety, general environmental impacts of products,
and waste streams are studied, and pollution prevention Four case studies are presented below which exemplify
concepts are formulated. the role of the structured pollution prevention program
During laboratory studies, reaction chemistry is con- methodology, the value of quickly defining the incen-
firmed, waste streams are characterized, process variables tive for pollution prevention using the cost of end-of-pipe
are tested, pollution prevention options are identified, treatment, and the benefits of using the waste stream and
data are collected for the pilot plant and process design, process analyses to parse the problem at hand. Five case
and the potential impact of environmental regulations is studies are also presented illustrating pollution prevention
determined. results at each of the stages described in Fig. 11.
During pilot plant studies, laboratory results are con-
firmed, process chemistry is finalized, key process vari- A. Program Elements—U.S. EPA and
ables are tested, equipment design is evaluated, and waste DuPont Chambers Works Waste
characteristics are defined. It is especially important at Minimization Project
this stage of R&D that all major environmental cost areas In May 1993, the U.S. EPA and DuPont completed a joint
are understood as these relate to the overall viability of a
2-year project to identify waste reduction options at the
commercial project.
DuPont Chambers Works site in Deepwater, New Jersey.
The project had three primary goals as conceived:
B. Pollution Prevention during Process
and Design Engineering
1. Identify methods for the actual reduction or
While the greatest opportunity for cost-effective waste re- prevention of pollution for specific chemical
duction at the source exists at the R&D stage, additional processes at the Chambers Works site.