Page 127 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 127
P1: FPP Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-85 May 17, 2001 20:35
Catalysis, Homogeneous 475
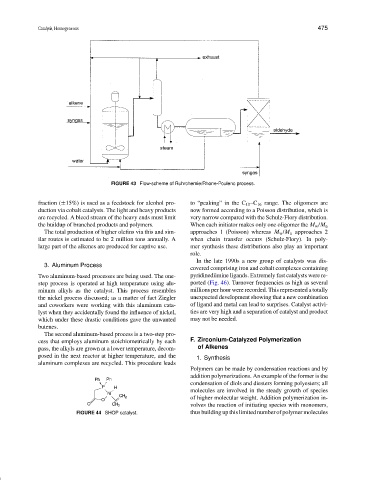
FIGURE 43 Flow-scheme of Ruhrchemie/Rhone-Poulenc process.
fraction (±15%) is used as a feedstock for alcohol pro- to “peaking” in the C 10 –C 16 range. The oligomers are
duction via cobalt catalysts. The light and heavy products now formed according to a Poisson distribution, which is
are recycled. A bleed stream of the heavy ends must limit very narrow compared with the Schulz-Flory distribution.
the buildup of branched products and polymers. When each initiator makes only one oligomer the M w /M n
The total production of higher olefins via this and sim- approaches 1 (Poisson) whereas M w /M n approaches 2
ilar routes is estimated to be 2 million tons annually. A when chain transfer occurs (Schulz-Flory). In poly-
large part of the alkenes are produced for captive use. mer synthesis these distributions also play an important
role.
In the late 1990s a new group of catalysts was dis-
3. Aluminum Process
covered comprising iron and cobalt complexes containing
Two aluminum-based processes are being used. The one- pyridinediimine ligands. Extremely fast catalysts were re-
step process is operated at high temperature using alu- ported (Fig. 46). Turnover frequencies as high as several
minum alkyls as the catalyst. This process resembles millions per hour were recorded. This represented a totally
the nickel process discussed; as a matter of fact Ziegler unexpected development showing that a new combination
and coworkers were working with this aluminum cata- of ligand and metal can lead to surprises. Catalyst activi-
lyst when they accidentally found the influence of nickel, ties are very high and a separation of catalyst and product
which under these drastic conditions gave the unwanted may not be needed.
butenes.
The second aluminum-based process is a two-step pro-
cess that employs aluminum stoichiometrically by each F. Zirconium-Catalyzed Polymerization
pass, the alkyls are grown at a lower temperature, decom- of Alkenes
posed in the next reactor at higher temperature, and the 1. Synthesis
aluminum complexes are recycled. This procedure leads
Polymers can be made by condensation reactions and by
addition polymerizations. An example of the former is the
condensation of diols and diesters forming polyesters; all
molecules are involved in the steady growth of species
of higher molecular weight. Addition polymerization in-
volves the reaction of initiating species with monomers,
FIGURE 44 SHOP catalyst. thus building up this limited number of polymer molecules