Page 126 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 126
P1: FPP Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-85 May 17, 2001 20:35
474 Catalysis, Homogeneous
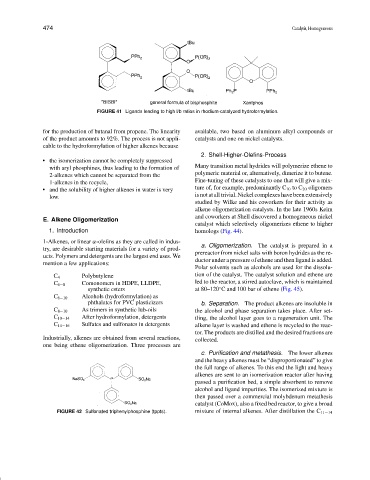
FIGURE 41 Ligands leading to high l/b ratios in rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation.
for the production of butanal from propene. The linearity available, two based on aluminum alkyl compounds or
of the product amounts to 92%. The process is not appli- catalysts and one on nickel catalysts.
cable to the hydroformylation of higher alkenes because
2. Shell-Higher-Olefins-Process
the isomerization cannot be completely suppressed
with aryl phosphines, thus leading to the formation of Many transition metal hydrides will polymerize ethene to
2-alkenes which cannot be separated from the polymeric material or, alternatively, dimerize it to butene.
1-alkenes in the recycle, Fine-tuning of these catalysts to one that will give a mix-
and the solubility of higher alkenes in water is very ture of, for example, predominantly C 10 to C 20 oligomers
low. is not at all trivial. Nickel complexes have been extensively
studied by Wilke and his coworkers for their activity as
alkene oligomerization catalysts. In the late 1960s Keim
and coworkers at Shell discovered a homogeneous nickel
E. Alkene Oligomerization
catalyst which selectively oligomerizes ethene to higher
1. Introduction homologs (Fig. 44).
1-Alkenes, or linear α-olefins as they are called in indus-
a. Oligomerization. The catalyst is prepared in a
try, are desirable starting materials for a variety of prod-
prereactor from nickel salts with boron hydrides as the re-
ucts. Polymers and detergents are the largest end uses. We
ductor under a pressure of ethene and then ligand is added.
mention a few applications:
Polar solvents such as alcohols are used for the dissolu-
Polybutylene tion of the catalyst. The catalyst solution and ethene are
C 4
Comonomers in HDPE, LLDPE, led to the reactor, a stirred autoclave, which is maintained
C 6−8
◦
synthetic esters at 80–120 C and 100 bar of ethene (Fig. 45).
Alcohols (hydroformylation) as
C 6−10
phthalates for PVC plasticizers b. Separation. The product alkenes are insoluble in
As trimers in synthetic lub-oils
C 8−10 the alcohol and phase separation takes place. After set-
After hydroformylation, detergents
C 10−14 tling, the alcohol layer goes to a regeneration unit. The
Sulfates and sulfonates in detergents
C 14−16 alkene layer is washed and ethene is recycled to the reac-
tor. The products are distilled and the desired fractions are
Industrially, alkenes are obtained from several reactions, collected.
one being ethene oligomerization. Three processes are
c. Purification and metathesis. The lower alkenes
and the heavy alkenes must be “disproportionated” to give
the full range of alkenes. To this end the light and heavy
alkenes are sent to an isomerization reactor after having
passed a purification bed, a simple absorbent to remove
alcohol and ligand impurities. The isomerized mixture is
then passed over a commercial molybdenum metathesis
catalyst (CoMox), also a fixed bed reactor, to give a broad
FIGURE 42 Sulfonated triphenylphosphine (tppts). mixture of internal alkenes. After distillation the C 11−14