Page 168 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 168
P1: GOL Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007F-314 July 6, 2001 16:59
324 Heterocyclic Chemistry
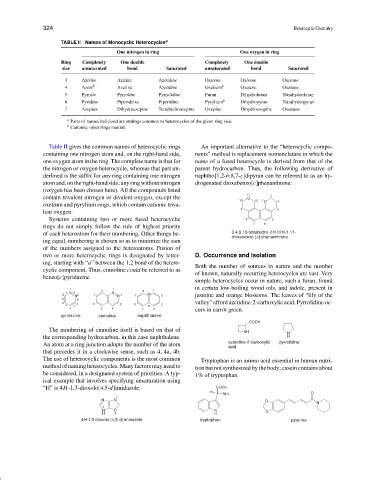
TABLE II Names of Monocyclic Heterocycles a
One nitrogen in ring One oxygen in ring
Ring Completely One double Completely One double
size unsaturated bond Saturated unsaturated bond Saturated
3 Azirine Azirine Aziridine Oxirene Oxirene Oxirane
4 Azete b Azetine Azetidine Oxetium b Oxetene Oxetane
5 Pyrrole Pyrroline Pyrrolidine Furan Dihydrofuran Tetrahydrofuran
6 Pyridine Piperideine Piperidine Pyrylium b Dihydropyran Tetrahydropyran
7 Azepine Dihydroazepine Tetrahydroazepine Oxepine Dihydrooxepine Oxepane
a Parts of names italicized are endings common to heterocycles of the given ring size.
b Cationic; other rings neutral.
Table II gives the common names of heterocyclic rings An important alternative to the “heterocyclic compo-
containing one nitrogen atom and, on the right-hand side, nents” method is replacement nomenclature in which the
one oxygen atom in the ring. The complete name is that for name of a fused heterocycle is derived from that of the
the nitrogen or oxygen heterocycle, whereas that part un- parent hydrocarbon. Thus, the following derivative of
derlined is the suffix for any ring containing one nitrogen naphtho[1,2-b:8,7-c]dipyran can be referred to as an hy-
atom and, on the right-hand side, any ring without nitrogen drogenated dioxabenzo[c]phenanthrene:
(oxygen has been chosen here). All the compounds listed
11
contain trivalent nitrogen or divalent oxygen, except the O 2
10 12 1 O 3
oxetium and pyrylium rings, which contain cationic triva-
9 4
lent oxygen.
Systems containing two or more fused heterocyclic 8 5
7 6
rings do not simply follow the rule of highest priority
of each heteroatom for their numbering. Other things be- 3,4,9,10-tetrahydro-2H,12H-1,11-
dioxabenzo [c] phenanthrene
ing equal, numbering is chosen so as to minimize the sum
of the numbers assigned to the heteroatoms. Fusion of
two or more heterocyclic rings is designated by letter- D. Occurrence and Isolation
ing, starting with “a” between the 1,2 bond of the hetero-
Both the number of sources in nature and the number
cyclic component. Thus, cinnoline could be referred to as
of known, naturally occurring heterocycles are vast. Very
benzo[c]pyridazine.
simple heterocycles occur in nature, such a furan, found
in certain low-boiling wood oils, and indole, present in
1 8 1 8 1
f N a N
6 N 2 7 N 2 7 8a 2 jasmine and orange blossoms. The leaves of “lily of the
e b
5 3 6 3 6 3 valley” afford azetidine-2-carboxylic acid. Pyrrolidine oc-
d c 4a
4 5 4 5 4 curs in carrot green.
pyridazine cinnoline naphthalene
COOH
The numbering of cinnoline itself is based on that of NH N
the corresponding hydrocarbon, in this case naphthalene. H
An atom at a ring junction adopts the number of the atom azetidine-2-carboxylic pyrrolidine
acid
that precedes it in a clockwise sense, such as 4, 4a, 4b.
The use of heterocyclic components is the most common Tryptophan is an amino acid essential in human nutri-
method of naming heterocycles. Many factors may need to tion but not synthesized by the body; casein contains about
be considered, in a designated system of priorities. A typ- 1% of tryptophan.
ical example that involves specifying unsaturation using
“H” is 4H-1,3-dioxolo[4,5-d]imidazole. COOH
H O
NH 2
1
N O O
N
4
N O N O
H 3 H
4H-1,3-dioxolo [4,5-d] imidazole tryptophan piperine