Page 212 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 212
P1: GPJ/GLT P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en011-542 July 26, 2001 15:33
498 Organic Chemistry, Synthesis
Limitations of space restrict this article to highlights As with fluorination, a mixture of products is formed. Pho-
from this diverse field. Throughout the discussion, name tochemically induced iodination suffers from side reac-
reactions and procedures are cited in parentheses. tions resulting from the hydrogen iodide formed.
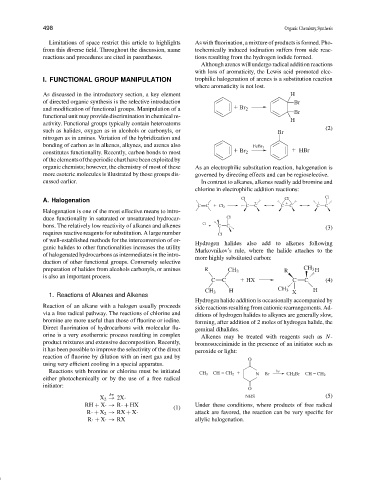
Although arenes will undergo radical addition reactions
with loss of aromaticity, the Lewis acid promoted elec-
I. FUNCTIONAL GROUP MANIPULATION trophilic halogenation of arenes is a substitution reaction
where aromaticity is not lost.
As discussed in the introductory section, a key element H
of directed organic synthesis is the selective introduction Br
and modification of functional groups. Manipulation of a Br 2
Br
functional unit may provide discrimination in chemical re-
H
activity. Functional groups typically contain heteroatoms
(2)
such as halides, oxygen as in alcohols or carbonyls, or Br
nitrogen as in amines. Variation of the hybridization and
bonding of carbon as in alkenes, alkynes, and arenes also FeBr 3
constitutes functionality. Recently, carbon bonds to most Br 2 HBr
oftheelementsoftheperiodiccharthavebeenexploitedby
organic chemists; however, the chemistry of most of these As an electrophilic substitution reaction, halogenation is
more esoteric molecules is illustrated by those groups dis- governed by directing effects and can be regioselective.
cussed earlier. In contrast to alkanes, alkenes readily add bromine and
chlorine in electrophilic addition reactions:
Cl
Cl
Cl
A. Halogenation
C C Cl 2 C C C C C C
Halogenation is one of the most effective means to intro-
duce functionality in saturated or unsaturated hydrocar- Cl
bons. The relatively low reactivity of alkanes and alkenes Cl C C (3)
requires reactive reagents for substitution. A large number Cl
of well-established methods for the interconversion of or-
Hydrogen halides also add to alkenes following
ganic halides to other functionalities increases the utility
Markovnikov’s rule, where the halide attaches to the
of halogenated hydrocarbons as intermediates in the intro-
more highly substituted carbon:
duction of other functional groups. Conversely selective
preparation of halides from alcohols carbonyls, or amines R CH 3 R CH 3 H
is also an important process.
C C HX C C (4)
CH 3 H CH 3 X H
1. Reactions of Alkanes and Alkenes
Hydrogen halide addition is occasionally accompanied by
Reaction of an alkane with a halogen usually proceeds side reactions resulting from cationic rearrangements. Ad-
via a free radical pathway. The reactions of chlorine and ditions of hydrogen halides to alkynes are generally slow,
bromine are more useful than those of fluorine or iodine. forming, after addition of 2 moles of hydrogen halide, the
Direct fluorination of hydrocarbons with molecular flu- geminal dihalides.
orine is a very exothermic process resulting in complex Alkenes may be treated with reagents such as N-
product mixtures and extensive decomposition. Recently, bromosuccinimide in the presence of an initiator such as
it has been possible to improve the selectivity of the direct peroxide or light:
reaction of fluorine by dilution with an inert gas and by
O
using very efficient cooling in a special apparatus.
Reactions with bromine or chlorine must be initiated CH 3 CH CH 2 N Br hv CH 2 Br CH CH 2
either photochemically or by the use of a free radical
initiator:
O
hν NBS (5)
X 2 → 2X·
RH + X·→ R·+ HX Under these conditions, where products of free radical
(1)
R·+ X 2 → RX + X· attack are favored, the reaction can be very specific for
R·+ X·→ RX allylic halogenation.