Page 247 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 247
P1: GJC/GLE P2: GNB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN011A-544 July 25, 2001 18:30
534 Organometallic Chemistry
3
5
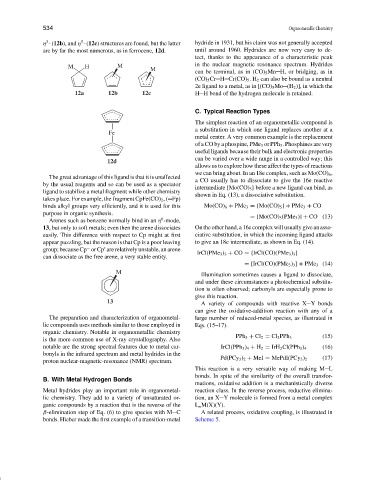
η - (12b), and η - (12c) structures are found, but the latter hydride in 1931, but his claim was not generally accepted
are by far the most numerous, as in ferrocene, 12d. until around 1960. Hydrides are now very easy to de-
tect, thanks to the appearance of a characteristic peak
M H M in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum. Hydrides
M
can be terminal, as in (CO) 5 Mn H, or bridging, as in
(CO) 5 Cr H Cr(CO) 5 . H 2 can also be bound as a neutral
2e ligand to a metal, as in [(CO) 5 Mo (H 2 )], in which the
12a 12b 12c H H bond of the hydrogen molecule is retained.
C. Typical Reaction Types
The simplest reaction of an organometallic compound is
a substitution in which one ligand replaces another at a
Fe
metal center. A very common example is the replacement
of a CO by a phospine, PMe 3 or PPh 3 . Phosphines are very
useful ligands because their bulk and electronic properties
can be varied over a wide range in a controlled way; this
12d
allows us to explore how these affect the types of reactions
we can bring about. In an 18e complex, such as Mo(CO) 6 ,
The great advantage of this ligand is that it is unaffected
a CO usually has to dissociate to give the 16e reactive
by the usual reagents and so can be used as a spectator
intermediate {Mo(CO) 5 } before a new ligand can bind, as
ligand to stabilize a metal fragment while other chemistry
shown in Eq. (13), a dissociative substitution.
takes place. For example, the fragment CpFe(CO) 2 ,( Fp)
binds alkyl groups very efficiently, and it is used for this Mo(CO) 6 + PMe 3 = {Mo(CO) 5 }+ PMe 3 + CO
purpose in organic synthesis. = [Mo(CO) 5 (PMe 3 )] + CO (13)
6
Arenes such as benzene normally bind in an η -mode,
13, but only to soft metals; even then the arene dissociates On the other hand, a 16e complex will usually give an asso-
easily. This difference with respect to Cp might at first ciative substitution, in which the incoming ligand attacks
appear puzzling, but the reason is that Cp is a poor leaving to give an 18e intermediate, as shown in Eq. (14).
− •
group; because Cp or Cp are relatively unstable, an arene
IrCl(PMe 3 ) 3 + CO = {IrCl(CO)(PMe 3 ) 3 }
can dissociate as the free arene, a very stable entity.
= [IrCl(CO)(PMe 3 ) 3 ] + PMe 3 (14)
M
Illumination sometimes causes a ligand to dissociate,
and under these circumstances a photochemical substitu-
tion is often observed; carbonyls are especially prone to
give this reaction.
13 A variety of compounds with reactive X Y bonds
can give the oxidative-addition reaction with any of a
The preparation and characterization of organometal- large number of reduced-metal species, as illustrated in
lic compounds uses methods similar to those employed in Eqs. (15–17).
organic chemistry. Notable in organometallic chemistry
is the more common use of X-ray crystallography. Also PPh 3 + Cl 2 = Cl 2 PPh 3 (15)
notable are the strong spectral features due to metal car- IrCl(PPh 3 ) 4 + H 2 = IrH 2 Cl(PPh 3 ) 4 (16)
bonyls in the infrared spectrum and metal hydrides in the
proton nuclear-magnetic-resonance (NMR) spectrum. Pd(PCy 3 ) 2 + MeI = MePdI(PCy 3 ) 2 (17)
This reaction is a very versatile way of making M L
bonds. In spite of the similarity of the overall transfor-
B. With Metal Hydrogen Bonds
mations, oxidative addition is a mechanistically diverse
Metal hydrides play an important role in organometal- reaction class. In the reverse process, reductive elimina-
lic chemistry. They add to a variety of unsaturated or- tion, an X Y molecule is formed from a metal complex
ganic compounds by a reaction that is the reverse of the L n M(X)(Y).
β-elimination step of Eq. (6) to give species with M C A related process, oxidative coupling, is illustrated in
bonds. Hieber made the first example of a transition-metal Scheme 5.