Page 248 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 248
P1: GJC/GLE P2: GNB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN011A-544 July 25, 2001 18:30
Organometallic Chemistry 535
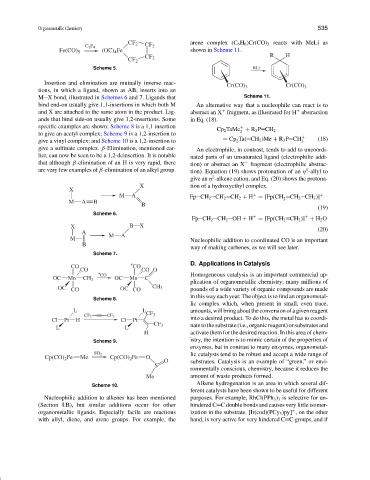
arene complex (C 6 H 6 )Cr(CO) 3 reacts with MeLi as
CF 2
C 2 F 4 CF 2
(OC) 4 Fe shown in Scheme 11.
Fe(CO) 5
R H
CF 2
CF 2
Scheme 5. RLi
Insertion and elimination are mutually inverse reac-
Cr(CO) 3 Cr(CO) 3
tions, in which a ligand, shown as AB, inserts into an
M X bond, illustrated in Schemes 6 and 7. Ligands that Scheme 11.
bind end-on usually give 1,1-insertions in which both M An alternative way that a nucleophile can react is to
and X are attached to the same atom in the product. Lig- abstract an X fragment, as illustrated for H abstraction
+
+
ands that bind side-on usually give 1,2-insertions. Some in Eq. (18).
specific examples are shown: Scheme 8 is a 1,1 insertion +
Cp 2 TaMe + R 3 P CH 2
2
to give an acetyl complex; Scheme 9 is a 1,2-insertion to
= Cp Ta( CH 2 )Me + R 3 P CH + (18)
give a vinyl complex; and Scheme 10 is a 1,2-insertion to 2 3
give a sulfinate complex. β-Elimination, mentioned ear- An electrophile, in contrast, tends to add to uncoordi-
lier, can now be seen to be a 1,2-deinsertion. It is notable nated parts of an unsaturated ligand (electrophilic addi-
that although β-elimination of an H is very rapid, there tion) or abstract an X fragment (electrophilic abstrac-
−
are very few examples of β-elimination of an alkyl group. tion). Equation (19) shows protonation of an η -allyl to
1
2
give an η -alkene cation, and Eq. (20) shows the protona-
X tion of a hydroxyethyl complex.
X
M A Fp CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 + H = [Fp(CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 )] +
+
M A B
B
(19)
Scheme 6.
+
+
Fp CH 2 CH 2 OH + H = [Fp(CH 2 CH 2 )] + H 2 O
X B X
A (20)
M M A Nucleophilic addition to coordinated CO is an important
B
way of making carbenes, as we will see later.
Scheme 7.
D. Applications in Catalysis
*
CO CO
CO CO O
* CO Homogeneous catalysis is an important commercial ap-
OC Mn CH 3 OC Mn C
plication of organometallic chemistry; many millions of
OC CO OC CO CH 3 pounds of a wide variety of organic compounds are made
in this way each year. The object is to find an organometal-
Scheme 8.
lic complex which, when present in small, even trace,
L L amounts,willbringabouttheconversionofagivenreagent
CF 3
CF 3 CF 3
Cl Pt H Cl Pt into a desired product. To do this, the metal has to coordi-
CF 3 natetothesubstrate(i.e.,organicreagent)orsubstratesand
L L
H activate them for the desired reaction. In this area of chem-
Scheme 9. istry, the intention is to mimic certain of the properties of
enzymes, but in contrast to many enzymes, organometal-
SO 2 lic catalysts tend to be robust and accept a wide range of
Cp(CO) 2 Fe Me Cp(CO) 2 Fe O
O substrates. Catalysis is an example of “green,” or envi-
S
ronmentally conscious, chemistry, because it reduces the
Me amount of waste products formed.
Alkene hydrogenation is an area in which several dif-
Scheme 10.
ferent catalysts have been shown to be useful for different
Nucleophilic addition to alkenes has been mentioned purposes. For example, RhCl(PPh 3 ) 3 is selective for un-
(Section I.B), but similar additions occur for other hindered C C double bonds and causes very little isomer-
organometallic ligands. Especially facile are reactions ization in the substrate. [Ir(cod)(PCy 3 )py] , on the other
+
with allyl, diene, and arene groups. For example, the hand, is very active for very hindered C C groups, and if