Page 114 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 114
P1: GRB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005M-206 June 15, 2001 20:25
192 Electrochemistry
III
II
III
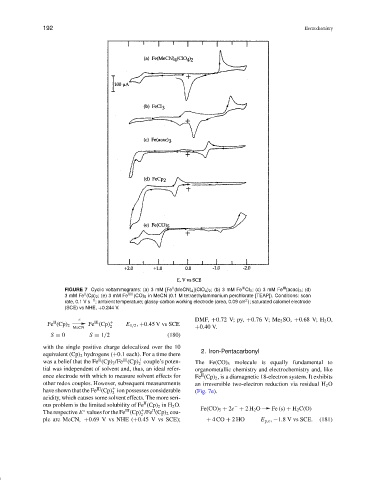
FIGURE 7 Cyclic voltammograms: (a) 3 mM [Fe (MeCN) 4 ](ClO 4 ) 2 ;(b)3mMFe Cl 3 ;(c)3mMFe (acac) 3 ; (d)
II
3mMFe (Cp) 2 ;(e)3mMFe VIII (CO) 5 in MeCN (0.1 M tetraethylammonium perchlorate [TEAP]). Conditions: scan
2
rate, 0.1 V s −1 ; ambient temperature; glassy-carbon working electrode (area, 0.09 cm ); saturated calomel electrode
(SCE) vs NHE, +0.244 V.
−e − DMF, +0.72 V; py, +0.76 V; Me 2 SO, +0.68 V; H 2 O,
II III +
Fe (Cp) 2 Fe (Cp) 2 E 1/2 , +0.45 V vs SCE
MeCN +0.40 V.
S = 0 S = 1/2 (180)
with the single positive charge delocalized over the 10
2. Iron-Pentacarbonyl
equivalent (Cp) 2 hydrogens (+0.1 each). For a time there
II
III
+
was a belief that the Fe (Cp) 2 /Fe (Cp) couple’s poten- The Fe(CO) 5 molecule is equally fundamental to
2
tial was independent of solvent and, thus, an ideal refer- organometallic chemistry and electrochemistry and, like
ence electrode with which to measure solvent effects for Fe (Cp) 2 , is a diamagnetic 18-electron system. It exhibits
II
other redox couples. However, subsequent measurements an irreversible two-electron reduction via residual H 2 O
III
have shown that the Fe (Cp) ion possesses considerable
+
2 (Fig. 7e).
acidity, which causes some solvent effects. The more seri-
II
ous problem is the limited solubility of Fe (Cp) 2 in H 2 O. Fe(CO) 5 + 2e + 2H 2 O Fe (s) + H 2 C(O)
−
III
II
◦
+
The respective E values for the Fe (Cp) /Fe (Cp) 2 cou-
2
ple are MeCN, +0.69 V vs NHE (+0.45 V vs SCE); + 4CO + 2HO − E p,c , −1.8VvsSCE. (181)