Page 111 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 111
P1: GRB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005M-206 June 15, 2001 20:25
Electrochemistry 189
PhCl 6 e [PhCl 6 ]
e , H 2 O
HPhCl 5 Cl HO
(165)
Hence, the PhCl 6 exhibits six irreversible two-electron
reductions (each product species less electrophilic than its
precursor) to yield at −2.8 V vs SCE benzene (PhH); an
overall 12-electron process.
−
PhCl 6 + 6H 2 O + 12e − PhH + 6Cl + 6HO −
(166)
Although such electrolyses are done in aprotic solvents
(e.g., DMF, DMSO, MeCN), even the most rigorously
dried solvent contains 3–20 mM H 2 O (50–350 ppm). If
the solvent has a degree of Brønsted acidity (e.g., alcohols
and ketones), then it can serve as a source of hydrogen
atoms.
TABLE VII Redox Potential for Alkyl Halides (RX ) and Aryl
Chlorides (Ar Cl x in Dimethyl Formamide at a Glassy Carbon
Electrode a
Alkyl halides
b
E p,c , VvsSCE c
RX I Br Cl
−2.10
CH 3−
−2.05 −2.41
n-C 4 H 9−
−1.92 −2.35
sec-C 4 H 9−
−1.78 −2.25
t-C 4 H 9−
−2.03 −2.48
c-C 6 H 11−
−1.68 −1.90
PhCH 2−
ClH 2 C− −2.05
Cl 2 HC− −1.99
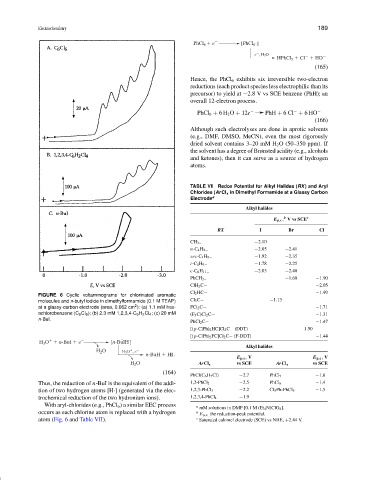
FIGURE 6 Cyclic voltammograms for chlorinated aromatic
molecules and n-butyl iodide in dimethylformamide (0.1 M TEAP) Cl 3 C− −1.13
2
at a glassy-carbon electrode (area, 0.062 cm ): (a) 1.1 mM hex- FCl 2 C− −1.71
achlorobenzene (C 6 Cl 6 ); (b) 2.3 mM 1,2,3,4-C 6 H 2 Cl 4 ; (c) 20 mM (F 3 C)Cl 2 C− −1.31
n-BuI.
PhCl 2 C− −1.47
[(p-ClPh) 2 HC]Cl 2 C− (DDT) −1.50
[(p-ClPh) 2 FC]Cl 2 C− (F-DDT) −1.44
H 3 O n-BuI e [n-BuIH ]
Alkyl halides
H 2 O H 3 O , e
n-BuH HI.
E p,c , V E p,c , V
H 2 O ArCl x vs SCE ArCl x vs SCE
(164)
PhCl(C 6 H 5 Cl) −2.7 PhCl 5 −1.6
Thus, the reduction of n-BuI is the equivalent of the addi- 1,2-PhCl 2 −2.5 PhCl 6 −1.4
tion of two hydrogen atoms [H·] (generated via the elec- 1,2,3-PhCl 3 −2.2 Cl 5 Ph-PhCl 5 −1.5
trochemical reduction of the two hydronium ions). 1,2,3,4-PhCl 4 −1.9
With aryl-chlorides (e.g., PhCl 6 ) a similar EEC process a
mM solutions in DMF [0.1 M (Et 4 N)ClO 4 ].
occurs as each chlorine atom is replaced with a hydrogen b E p,c, the reduction-peak potential.
atom (Fig. 6 and Table VII). c Saturated calomel electrode (SCE) vs NHE, +2.44 V.