Page 303 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 303
P1: GNH Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009N-447 July 19, 2001 23:3
820 Microwave Molecular Spectroscopy
the type of coupling, and various coupling cases are pos- synthesis of the many neutral molecules so far identified
sible depending on the origin of the electronic angular in interstellar space.
3
momentum. The stable O 2 molecule in a electronic Some other molecular ions that have been studied more
ground state is an important example that has been ex- recently are listed in Table XII. Some examples of ionic
tensively studied. It has a spin angular momentum of complexes are also included in the table. In some cases, the
analysis of the rotational spectrum was aided by the use of
1h and a zero electronic orbital angular momentum. O 2
does not have an electric dipole moment, but does have double resonance techniques or by information obtained
a magnetic moment associated with the spin angular mo- from ab initio calculations. Most ions have been positive
ment. The corresponding magnetic dipole transitions are, species (cation). Recently, the negative ion (anion) SH −
however, much weaker in general than electric dipole has been identified in the laboratory. The ion was produced
transitions. by the low-pressure electric discharge of H 2 S and argon.
Free radicals, like ions, play an important role in var- The measurement of this and other light hydrides has been
ious chemical reactions. The understanding of chemical aided by the availability of higher frequency microwave
−
mechanisms, whether associated with combustion, the in- sources. The first two transitions of SH fall at 0.56 and
terstellar medium, or other areas, can be clarified by de- 1.1 THz (see Section XI).
tection of radical intermediates.
Some recent studies of free radicals are given in
3. H-Bonded Complexes
Table XI. Here, we give the ground electronic state, per- and van der Waals Complexes
tinent comments, and structural parameters for some of
the radicals. The reader is directed to the references of the Microwave spectroscopy studies have provided consider-
table for a more detailed discussion of the experimental able information on the phenomenon of hydrogen bond-
methods and analysis of the rotational spectrum. A num- ing. Earlier studies with conventional microwave spec-
ber of interesting radicals are given in the table, such as trometers were on large H-bonded complexes. Typical
cyclicC 3 H,C n O,C 3 H,C n H,andHC 3 O.Also,wenotethat of these studies is the bimolecule trifluoroacetic acid–
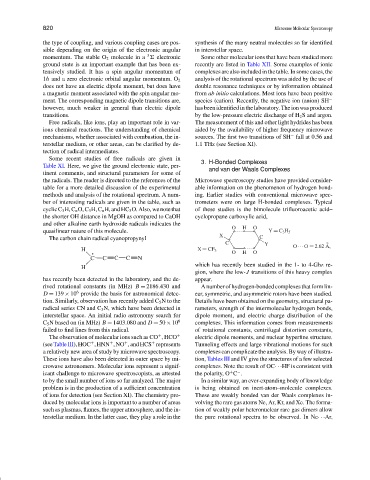
the shorter OH distance in MgOH as compared to CaOH cyclopropane carboxylic acid,
and other alkaline earth hydroxide radicals indicates the
O H O
quasilinear nature of this molecule. Y C 3 H 5
X
The carbon chain radical cyanopropynyl C
C Y O O 2.62 A,
°
H X CF 3
O H O
C C C C N
which has recently been studied in the 1- to 4-Ghz re-
H
gion, where the low-J transitions of this heavy complex
has recently been detected in the laboratory, and the de- appear.
rived rotational constants (in MHz) B = 2186.430 and A number of hydrogen-bonded complexes that form lin-
6
D = 139 × 10 provide the basis for astronomical detec- ear, symmetric, and asymmetric rotors have been studied.
tion. Similarly, observation has recently added C 5 N to the Details have been obtained on the geometry, structural pa-
radical series CN and C 3 N, which have been detected in rameters, strength of the intermolecular hydrogen bonds,
interstellar space. An initial radio astronomy search for dipole moment, and electric charge distribution of the
C 5 N based on (in MHz) B = 1403.080 and D = 50 × 10 6 complexes. This information comes from measurements
failed to find lines from this radical. of rotational constants, centrifugal distortion constants,
The observation of molecular ions such as CO , HCO + electric dipole moments, and nuclear hyperfine structure.
+
+
+
+
+
(seeTableIII),HOC ,HNN ,NO ,andHCS represents Tunneling effects and large vibrational motions for such
a relatively new area of study by microwave spectroscopy. complexes can complicate the analysis. By way of illustra-
These ions have also been detected in outer space by mi- tion, Tables III and IV give the structures of a few selected
crowave astronomers. Molecular ions represent a signif- complexes. Note the result of OC···HF is consistent with
−
+
icant challenge to microwave spectroscopists, as attested the polarity, O C .
to by the small number of ions so far analyzed. The major In a similar way, an ever-expanding body of knowledge
problem is in the production of a sufficient concentration is being obtained on inert-atom–molecule complexes.
of ions for detection (see Section XI). The chemistry pro- These are weakly bonded van der Waals complexes in-
duced by molecular ions is important to a number of areas volving the rare gas atoms Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe. The forma-
such as plasmas, flames, the upper atmosphere, and the in- tion of weakly polar heteronuclear rare gas dimers allow
terstellar medium. In the latter case, they play a role in the the pure rotational spectra to be observed. In Ne···Ar,