Page 397 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 397
P1: GTQ/GLE P2: GPJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012C-562 July 26, 2001 15:30
4 Photoacoustic Spectroscopy
modulated, only signals synchronized to the modulation IV. INSTRUMENTATION
are detected, and unwanted signals are eliminated.
2. Because it is insensitive to light scattering and light A. Modulated Photoacoustic Spectrometer
reflection properties of the sample (these features may re-
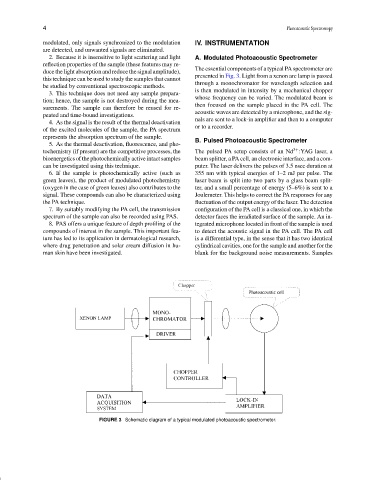
The essential components of a typical PA spectrometer are
duce the light absorption and reduce the signal amplitude),
presented in Fig. 3. Light from a xenon arc lamp is passed
this technique can be used to study the samples that cannot
through a monochromator for wavelength selection and
be studied by conventional spectroscopic methods.
is then modulated in intensity by a mechanical chopper
3. This technique does not need any sample prepara-
whose frequency can be varied. The modulated beam is
tion; hence, the sample is not destroyed during the mea-
then focused on the sample placed in the PA cell. The
surements. The sample can therefore be reused for re-
acoustic waves are detected by a microphone, and the sig-
peated and time-bound investigations.
nals are sent to a lock-in amplifier and then to a computer
4. As the signal is the result of the thermal deactivation
or to a recorder.
of the excited molecules of the sample, the PA spectrum
represents the absorption spectrum of the sample.
B. Pulsed Photoacoustic Spectrometer
5. As the thermal deactivation, fluorescence, and pho-
tochemistry (if present) are the competitive processes, the The pulsed PA setup consists of an Nd :YAG laser, a
3+
bioenergetics of the photochemically active intact samples beam splitter, a PA cell, an electronic interface, and a com-
can be investigated using this technique. puter. The laser delivers the pulses of 3.5 nsec duration at
6. If the sample is photochemically active (such as 355 nm with typical energies of 1–2 mJ per pulse. The
green leaves), the product of modulated photochemistry laser beam is split into two parts by a glass beam split-
(oxygen in the case of green leaves) also contributes to the ter, and a small percentage of energy (5–6%) is sent to a
signal. These compounds can also be characterized using Joulemeter. This helps to correct the PA responses for any
the PA technique. fluctuation of the output energy of the laser. The detection
7. By suitably modifying the PA cell, the transmission configuration of the PA cell is a classical one, in which the
spectrum of the sample can also be recorded using PAS. detector faces the irradiated surface of the sample. An in-
8. PAS offers a unique feature of depth profiling of the tegrated microphone located in front of the sample is used
compounds of interest in the sample. This important fea- to detect the acoustic signal in the PA cell. The PA cell
ture has led to its application in dermatological research, is a differential type, in the sense that it has two identical
where drug penetration and solar cream diffusion in hu- cylindrical cavities, one for the sample and another for the
man skin have been investigated. blank for the background noise measurements. Samples
FIGURE 3 Schematic diagram of a typical modulated photoacoustic spectrometer.