Page 400 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 400
P1: GTQ/GLE P2: GPJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012C-562 July 26, 2001 15:30
Photoacoustic Spectroscopy 7
determination of bond dissociation energies in complex, of tetracycline topically applied to skin. Tetracycline was
biologically important molecules. It has also proved to detected at 380 nm, where it strongly absorbs. The ease of
be a sensitive indicator of conformational distortions and identification of the substance in the spectral range sug-
mechanistic detail as biological molecules undergo reac- gests that penetration and distribution of other chemicals
tions. Using PAS, melanin content has been determined in through the skin can also be investigated by FTIR–PAS.
human hair samples. A recent study reports a novel percutaneous absorptio-
metric system using an open-ended PA cell combined with
C. Dermatology a light guide. This system is capable of measuring the de-
crease of the amount of a drug over the skin in vivo at any
Skin forms a protective boundary layer between the body
given site with great ease, high sensitivity, and accuracy.
and its environment. With respect to transport proper-
Using the UV laser PA method, it demonstrates a series
ties, the nonvascularized epidermis, the outermost layer
of in vivo and in vitro percutaneous absorptiometric mea-
of which is formed by the stratum corneum (SC), serves
surements in the presence of anti-inflammatory and anti-
as a barrier for the body. In the underlying vascularized
itching agents. Melanin nonradiative de-excitation states
dermis, the transport properties are strongly influenced by
and skin lipids have also been investigated in human skin
blood circulation.
samples.
As mentioned earlier, PAS is a good tool for studying
Using PAS, the influence of SC constituents such as
the optical and thermal properties of a sample. Hence,
water, lipids, and hydrophilic substances on UV light ab-
this technique can be applied to fields of dermatological
sorption have been investigated. The data reveal that upon
research such as drug detection and drug diffusion studies
hydration of SC, there is a decrease of UV absorption coef-
in skin, and thermal properties and water content of the
ficient by about 20%. Lipids were not shown to have any
skin. The optical and thermal properties of the sample are
direct effect on UV absorption by SC. Further, the data
characterized by the optical absorption distance, µ β , and
suggest that the hydrophilic substances of SC were pro-
the thermal diffusion distance, µ s . The optical absorption
tected in situ by polar lipids enmeshed within the structure
distance is the inverse of the optical absorption coefficient
of SC.
β. The thermal diffusion length is defined by
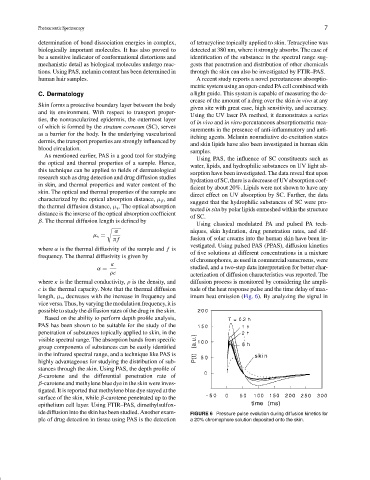
Using classical modulated PA and pulsed PA tech-
α niques, skin hydration, drug penetration rates, and dif-
µ s =
π f fusion of solar creams into the human skin have been in-
vestigated. Using pulsed PAS (PPAS), diffusion kinetics
where α is the thermal diffusivity of the sample and f is
of five solutions at different concentrations in a mixture
frequency. The thermal diffusivity is given by
of chromophores, as used in commercial sunscreens, were
κ
α = studied, and a two-step data interpretation for better char-
ρc acterization of diffusion characteristics was reported. The
where κ is the thermal conductivity, ρ is the density, and diffusion process is monitored by considering the ampli-
c is the thermal capacity. Note that the thermal diffusion tude of the heat response pulse and the time delay of max-
length, µ s , decreases with the increase in frequency and imum heat emission (Fig. 6). By analyzing the signal in
viceversa.Thus,byvaryingthemodulationfrequency,itis
possible to study the diffusion rates of the drug in the skin.
Based on the ability to perform depth profile analysis,
PAS has been shown to be suitable for the study of the
penetration of substances topically applied to skin, in the
visible spectral range. The absorption bands from specific
group components of substances can be easily identified
in the infrared spectral range, and a technique like PAS is
highly advantageous for studying the distribution of sub-
stances through the skin. Using PAS, the depth profile of
β-carotene and the differential penetration rate of
β-carotene and methylene blue dye in the skin were inves-
tigated. It is reported that methylene blue dye stayed at the
surface of the skin, while β-carotene penetrated up to the
epithelium cell layer. Using FTIR–PAS, dimethylsulfox-
ide diffusion into the skin has been studied. Another exam- FIGURE 6 Pressure pulse evolution during diffusion kinetics for
ple of drug detection in tissue using PAS is the detection a 20% chromophore solution deposited onto the skin.