Page 5 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 5
P1: GJB Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En001f25 May 7, 2001 13:58
544 Analytical Chemistry
elements in alloy steels to part-per-billion levels of drugs ganic species lies in their chemical and physical behavior.
in biological tissue, are handled by the analyst. The field For example, reagents are used to yield distinct chemical
is founded on the conversion of a measured physical prop- effects such as the production of colored solutions or pre-
erty of the species being examined to a usable signal. It cipitates, the generation of easily observed gases, and the
is generally divided into two categories, classical and in- dissolution of previously insoluble substances. In a typical
strumental, on the basis of its historical development. The analysis, the identification of several species is required,
overall strategy is to prepare a sample correctly, choose and in this circumstance, it is desirable to employ selective
a particular method of analysis, and report the results reactions for each component of the system.
in a meaningful format, which may include a statistical This type of chemistry is incorporated into a strategy
evaluation. that involves the separation of the original mixture into
several parts in order to avoid the buildup of a highly
complex array with a specific sample due to the addition
of a number of reagents. Each part is then subjected to
I. CLASSICAL METHODS
an analysis of a small number of species. In summary,
the analysis involves a set of sequenced separations and
A. Semimicro Qualitative Analysis
identifications.
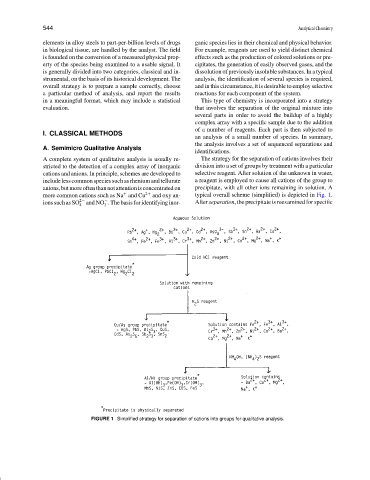
A complete system of qualitative analysis is usually re- The strategy for the separation of cations involves their
stricted to the detection of a complex array of inorganic division into a set of groups by treatment with a particular
cations and anions. In principle, schemes are developed to selective reagent. After solution of the unknown in water,
include less common species such as rhenium and tellurate a reagent is employed to cause all cations of the group to
anions,butmoreoftenthannotattentionisconcentratedon precipitate, with all other ions remaining in solution. A
more common cations such as Na and Cu 2+ and oxy an- typical overall scheme (simplified) is depicted in Fig. 1.
+
ionssuchasSO 2− andNO .Thebasisforidentifyinginor- After separation, the precipitate is reexamined for specific
−
4 3
FIGURE 1 Simplified strategy for separation of cations into groups for qualitative analysis.