Page 154 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 154
P1: GPB/GLT P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012f-594 July 26, 2001 11:9
662 Polymers, Ferroelectric
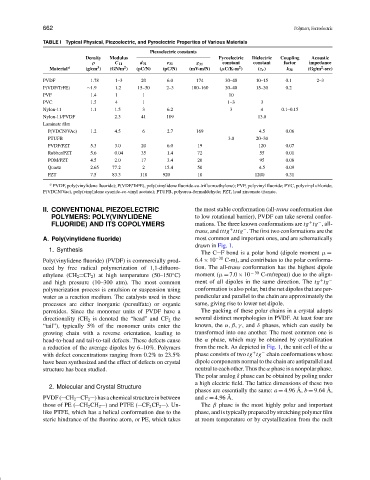
TABLE I Typical Physical, Piezoelectric, and Pyroelectric Properties of Various Materials
Piezoelectric constants
Density Modulus Pyroelectric Dielectric Coupling Acoustic
ρ C 11 d 31 e 31 g 31 constant constant factor impedance
2
2
2
3
Material a (g/cm ) (GN/m ) (pC/N) (pC/N) (mV-m/N) (µC/K-m ) (ε r ) k 31 (Gg/m -sec)
PVDF 1.78 1–3 20 6.0 174 30–40 10–15 0.1 2–3
P(VDF/TrFE) ∼1.9 1.2 15–30 2–3 100–160 30–40 15–30 0.2
PVF 1.4 1 1 10
PVC 1.5 4 1 1–3 3
Nylon-11 1.1 1.5 3 6.2 3 4 0.1–0.15
Nylon-11/PVDF 2.3 41 109 13.8
Laminate film
P(VDCN/VAc) 1.2 4.5 6 2.7 169 4.5 0.06
PTUFB 3.0 20–30
PVDF/PZT 5.3 3.0 20 6.0 19 120 0.07
Rubber/PZT 5.6 0.04 35 1.4 72 55 0.01
POM/PZT 4.5 2.0 17 3.4 20 95 0.08
Quartz 2.65 77.2 2 15.4 50 4.5 0.09
PZT 7.5 83.3 110 920 10 1200 0.31
a PVDF, poly(vinylidene fluoride); P(VDF/TrFE), poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene); PVF, polyvinyl fluoride; PVC, polyvinyl chloride;
P(VDCN/Vac), poly(vinylidene cyanide-co-vinyl acetate); PTUFB, polyurea–formaldehyde; PZT, lead zirconate titanate.
II. CONVENTIONAL PIEZOELECTRIC the most stable conformation (all-trans conformation due
POLYMERS: POLY(VINYLIDENE to low rotational barrier), PVDF can take several confor-
FLUORIDE) AND ITS COPOLYMERS mations. The three known conformations are tg tg , all-
+
−
trans, and tttg tttg . The first two conformations are the
−
+
A. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) most common and important ones, and are schematically
drawn in Fig. 1.
1. Synthesis
The C F bond is a polar bond (dipole moment µ =
Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) is commercially prod- 6.4 × 10 −30 C-m), and contributes to the polar conforma-
uced by free radical polymerization of 1,1-difluoro- tion. The all-trans conformation has the highest dipole
ethylene (CH 2 CF 2 ) at high temperature (50–150 C) moment (µ = 7.0 × 10 − 30 C-m/repeat) due to the align-
◦
+
and high pressure (10–300 atm). The most common ment of all dipoles in the same direction. The tg tg −
polymerization process is emulsion or suspension using conformation is also polar, but the net dipoles that are per-
water as a reaction medium. The catalysts used in these pendicular and parallel to the chain are approximately the
processes are either inorganic (persulfate) or organic same, giving rise to lower net dipole.
peroxides. Since the monomer units of PVDF have a The packing of these polar chains in a crystal adopts
directionality (CH 2 is denoted the “head” and CF 2 the several distinct morphologies in PVDF. At least four are
“tail”), typically 5% of the monomer units enter the known, the α, β, γ , and δ phases, which can easily be
growing chain with a reverse orientation, leading to transformed into one another. The most common one is
head-to-head and tail-to-tail defects. These defects cause the α phase, which may be obtained by crystallization
a reduction of the average dipoles by 6–10%. Polymers from the melt. As depicted in Fig. 1, the unit cell of the α
−
+
with defect concentrations ranging from 0.2% to 23.5% phase consists of two tg tg chain conformations whose
have been synthesized and the effect of defects on crystal dipole components normal to the chain are antiparallel and
structure has been studied. neutral to each other. Thus the α phase is a nonpolar phase.
The polar analog δ phase can be obtained by poling under
a high electric field. The lattice dimensions of these two
2. Molecular and Crystal Structure
˚
˚
phases are essentially the same: a = 4.96 A, b = 9.64 A,
˚
PVDF ( CH 2 CF 2 ) has a chemical structure in between and c = 4.96 A.
those of PE ( CH 2 CH 2 ) and PTFE ( CF 2 CF 2 ). Un- The β phase is the most highly polar and important
like PTFE, which has a helical conformation due to the phase, and is typically prepared by stretching polymer film
steric hindrance of the fluorine atom, or PE, which takes at room temperature or by crystallization from the melt