Page 159 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 159
P1: GPB/GLT P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012f-594 July 26, 2001 11:9
Polymers, Ferroelectric 667
TABLE II A Summary of VDF/TrFE/CTFE Terpolymers Prepared by Borane/Oxygen Initiator a
Terpolymer Melting Phase transition
mole ratio temperature temperature
[η]
Sample T m ∆H m T C ∆H C (MEK) b P max E c Dielectric Dielectric
2
no. VDF TrFE CTFE ( C) (J/g) ( C) (J/g) (35 C) (mC/m ) (MV/m) constant c loss
◦
◦
◦
1 72.2 17.8 10.0 107.8 17.8 25.0 0.4 0.38 82 19.6 27.0 0.04
2 66.0 22.5 11.5 117.2 21.6 25.2 2.5 0.42 78 24.1 22.4 0.03
3 66.1 21.4 12.5 115.6 20.5 25.8 1.8 0.42 — — 40.9 0.04
4 63.1 25.4 11.5 113.7 18.5 None d None 0.49 76 19.8 53.5 0.06
5 61.4 25.3 13.3 111.3 17.8 15.6 1.5 0.69 75 33.7 53.1 0.06
6 58.0 33.1 8.9 130.0 21.3 31.6 2.5 0.63 63 16.4 33.0 0.05
7 60.0 36.0 4.0 140.9 25.7 43.8 6.5 0.58 87 21.8 26.4 0.04
8 55.6 36.1 8.3 124.6 21.2 None None 0.54 36 7.6 42.4 0.07
9 e 60.0 35.1 6.9 126.6 20.9 33.5 1.6 0.78 110 55.9 52.7 0.07
10 e 59.3 32.9 7.8 125.1 20.3 24.8 1.4 0.80 70 11.5 51.0 0.07
11 e 57.3 31.2 11.5 111.1 14.8 None None 0.75 45 39.4 50.5 0.06
a ◦ ◦
P max and E c at 100 MV/m, 10 Hz, 22 C. Dielectric constant and dielectric loss at 1 KHz, 22 C.
b
MEK, methylethylketone.
c
Value measured in the heating cycle.
d
None: no observable.
e
Sample prepared by constant monomer feed ratio during the polymerization.
the insertion of monomers in a preferred head-to-tail se- removed by methanol. Table II summarizes several
quence. No chain transfer and termination reactions are VDF/TrFE/CTFE terpolymers prepared by the same
expected during the propagating process, which will lead method. All terpolymers are high-molecular-weight
to a linear polymer structure with relatively narrow molec- (>20,000 g/mole) polymers with good solubility in com-
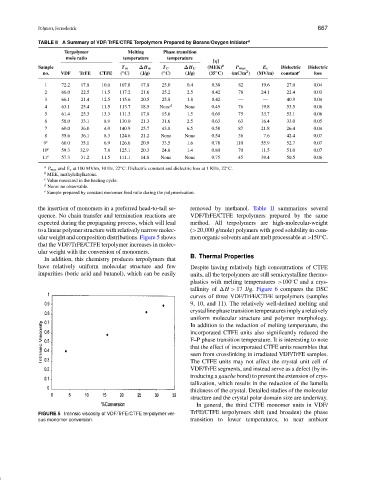
ular weight and composition distributions. Figure 5 shows mon organic solvents and are melt processable at >150 C.
◦
that the VDF/TrFE/CTFE terpolymer increases in molec-
ular weight with the conversion of monomers.
B. Thermal Properties
In addition, this chemistry produces terpolymers that
have relatively uniform molecular structure and few Despite having relatively high concentrations of CTFE
impurities (boric acid and butanol), which can be easily units, all the terpolymers are still semicrystalline thermo-
plastics with melting temperatures >100 C and a crys-
◦
tallinity of H > 17 J/g. Figure 6 compares the DSC
curves of three VDF/TrFE/CTFE terpolymers (samples
9, 10, and 11). The relatively well-defined melting and
crystalline phase transition temperatures imply arelatively
uniform molecular structure and polymer morphology.
In addition to the reduction of melting temperature, the
incorporated CTFE units also significantly reduced the
F–P phase transition temperature. It is interesting to note
that the effect of incorporated CTFE units resembles that
seen from crosslinking in irradiated VDF/TrFE samples.
The CTFE units may not affect the crystal unit cell of
VDF/TrFE segments, and instead serve as a defect (by in-
troducing a gauche bond) to prevent the extension of crys-
tallization, which results in the reduction of the lamella
thickness of the crystal. Detailed studies of the molecular
structure and the crystal polar domain size are underway.
In general, the third CTFE monomer units in VDF/
FIGURE 5 Intrinsic viscosity of VDF/TrFE/CTFE terpolymer ver- TrFE/CTFE terpolymers shift (and broaden) the phase
sus monomer conversion. transition to lower temperatures, to near ambient