Page 155 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 155
P1: GPB/GLT P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012f-594 July 26, 2001 11:9
Polymers, Ferroelectric 663
+
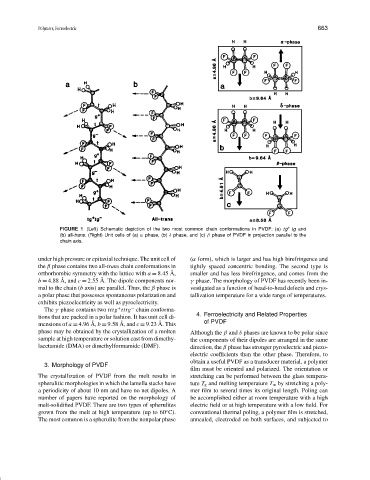
FIGURE 1 (Left) Schematic depiction of the two most common chain conformations in PVDF: (a) tg tg and
(b) all-trans. (Right) Unit cells of (a) α phase, (b) δ phase, and (c) β phase of PVDF in projection parallel to the
chain axis.
under high pressure or epitaxial technique. The unit cell of (α form), which is larger and has high birefringence and
the β phase contains two all-trans chain conformations in tightly spaced concentric bonding. The second type is
˚
orthorhombic symmetry with the lattice with a = 8.45 A, smaller and has less birefringence, and comes from the
˚
˚
b = 4.88 A, and c = 2.55 A. The dipole components nor- γ phase. The morphology of PVDF has recently been in-
mal to the chain (b axis) are parallel. Thus, the β phase is vestigated as a function of head-to-head defects and crys-
a polar phase that possesses spontaneous polarization and tallization temperature for a wide range of temperatures.
exhibits piezoelectricity as well as pyroelectricity.
+
The γ phase contains two tttg tttg chain conforma-
−
4. Ferroelectricity and Related Properties
tions that are packed in a polar fashion. It has unit cell di-
˚
˚
˚
mensions of a = 4.96 A, b = 9.58 A, and c = 9.23 A. This of PVDF
phase may be obtained by the crystallization of a molten Although the β and δ phases are known to be polar since
sample at high temperature or solution cast from dimethy- the components of their dipoles are arranged in the same
lacetamide (DMA) or dimethylformamide (DMF). direction, the β phase has stronger pyroelectric and piezo-
electric coefficients than the other phase. Therefore, to
obtain a useful PVDF as a transducer material, a polymer
3. Morphology of PVDF
film must be oriented and polarized. The orientation or
The crystallization of PVDF from the melt results in stretching can be performed between the glass tempera-
spherulitic morphologies in which the lamella stacks have ture T g and melting temperature T m by stretching a poly-
a periodicity of about 10 nm and have no net dipoles. A mer film to several times its original length. Poling can
number of papers have reported on the morphology of be accomplished either at room temperature with a high
melt-solidified PVDF. There are two types of spherulites electric field or at high temperature with a low field. For
grown from the melt at high temperature (up to 60 C). conventional thermal poling, a polymer film is stretched,
◦
The most common is a spherulite from the nonpolar phase annealed, electroded on both surfaces, and subjected to