Page 183 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 183
P1: GKY/MBQ P2: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012i-947 July 26, 2001 11:11
Polymers, Inorganic and Organometallic 691
ions replace Si(IV) in the lattice. Examples of 2D sheet
aluminosilicates are clays, micas, and talc. Feldspar and
zeolites (molecular sieves) are 3D network structures in
which AlO 4 and SiO 4 units share tetrahedral vertices. The
cavities created in these network polymers are accommo-
dated by cations such as Na and K . Depending on the
+
+
size of the cavity, these cations can be displaced by other
cations, hence their use as ion exchange materials. More-
over, by synthetically controlling the size and shape of
the cavity, small molecules like water, methanol, or gases
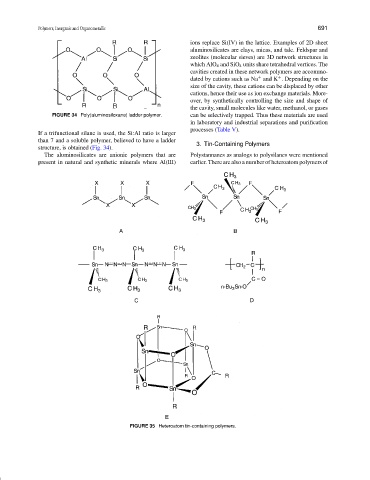
FIGURE 34 Poly(aluminosiloxane) ladder polymer. can be selectively trapped. Thus these materials are used
in laboratory and industrial separations and purification
processes (Table V).
If a trifunctional silane is used, the Si:Al ratio is larger
than 7 and a soluble polymer, believed to have a ladder
3. Tin-Containing Polymers
structure, is obtained (Fig. 34).
The aluminosilicates are anionic polymers that are Polystannanes as analogs to polysilanes were mentioned
present in natural and synthetic minerals where Al(III) earlier. There are also a number of heteroatom polymers of
FIGURE 35 Heteroatom tin-containing polymers.