Page 23 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 23
P1: FPP 2nd Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-64 May 19, 2001 20:39
Biopolymers 227
In many plant cell walls, the major hemicellulose is ei-
ther arabinoxylan—main chains of xylose with branches
of single arabinose residues on some of the xylose rings—
or glucuronoarabinoxylans with additional branches of
single unsubstituted or modified glucuronic acid residues
on some xylose rings.
Xyloglucans may act as food reserves in seeds and have
a structural role in mature plants. They probably have ex-
tended ribbon-like structures. Xyloglucans have backbone
chains of β-(1 → 4)-linked glucose residues with xylose
units linked α-(1 → 6) as branches on some of the glucose
rings. Some branches can also contain galactose and fu-
cose residues but there seems to be no regular repeat in the
structure. This is a feature of many plant polysaccharides,
and the apparent lack of regularity may be necessary for
interaction with other proteins and polysaccharides in cell
walls which can, as a plant grows, elongate to many times
their original size. In addition, arabinoxyloglucans exist
in some plants, with arabinose units linked α-(1 → 2) to
xylose.
Glucomannans and the related galactoglucomannans
are important in softwood, and do not have a regular struc-
ture but have linear main chains containing, in an appar-
ently random order, both mannose and glucose joined
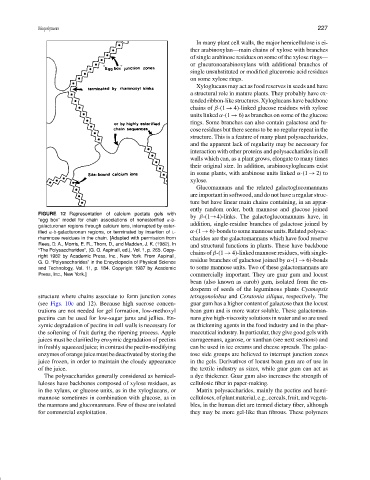
FIGURE 12 Representation of calcium pectate gels with
by β-(1→4)-links. The galactoglucomannans have, in
“egg box” model for chain associations of nonesterified α-D-
addition, single-residue branches of galactose joined by
galacturonan regions through calcium ions, interrupted by ester-
ified α-D-galacturonan regions, or terminated by insertion of L- α-(1 → 6)-bonds to some mannose units. Related polysac-
rhamnose residues in the chain. [Adapted with permission from charides are the galactomannans which have food reserve
Rees, D. A., Morris, E. R., Thom, D., and Madden, J. K. (1982). In and structural functions in plants. These have backbone
“The Polysaccharides”, (G. O. Aspinall, ed.), Vol. 1, p. 265. Copy- chains of β-(1 → 4)-linked mannose residues, with single-
right 1982 by Academic Press, Inc., New York. From Aspinall,
G. O. “Polysaccharides” in the Encyclopedia of Physical Science residue branches of galactose joined by α-(1 → 6)-bonds
and Technology, Vol. 11, p. 184. Copyright 1987 by Academic to some mannose units. Two of these galactomannans are
Press, Inc., New York.] commercially important. They are guar gum and locust
bean (also known as carob) gum, isolated from the en-
dosperm of seeds of the leguminous plants Cyamopsis
structure where chains associate to form junction zones tetragonolobus and Ceratonia siliqua, respectively. The
(see Figs. 10c and 12). Because high sucrose concen- guar gum has a higher content of galactose than the locust
trations are not needed for gel formation, low-methoxyl bean gum and is more water soluble. These galactoman-
pectins can be used for low-sugar jams and jellies. En- nans give high-viscosity solutions in water and so are used
zymic degradation of pectins in cell walls is necessary for as thickening agents in the food industry and in the phar-
the softening of fruit during the ripening process. Apple maceutical industry. In particular, they give good gels with
juices must be clarified by enzymic degradation of pectins carrageenans, agarose, or xanthan (see next sections) and
in freshly squeezed juice; in contrast the pectin-modifying can be used in ice creams and cheese spreads. The galac-
enzymes of orange juice must be deactivated by storing the tose side groups are believed to interrupt junction zones
juice frozen, in order to maintain the cloudy appearance in the gels. Derivatives of locust bean gum are of use in
of the juice. the textile industry as sizes, while guar gum can act as
The polysaccharides generally considered as hemicel- a dye thickener. Guar gum also increases the strength of
luloses have backbones composed of xylose residues, as cellulosic fiber in paper-making.
in the xylans, or glucose units, as in the xyloglucans, or Matrix polysaccharides, mainly the pectins and hemi-
mannose sometimes in combination with glucose, as in celluloses,ofplant material,e.g., cereals, fruit,and vegeta-
the mannans and glucomannans. Few of these are isolated bles, in the human diet are termed dietary fiber, although
for commercial exploitation. they may be more gel-like than fibrous. These polymers