Page 274 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 274
P1: GPQ Final Pages/GNB P2: GTV
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En012c-604 July 26, 2001 16:2
Polymers, Thermally Stable 783
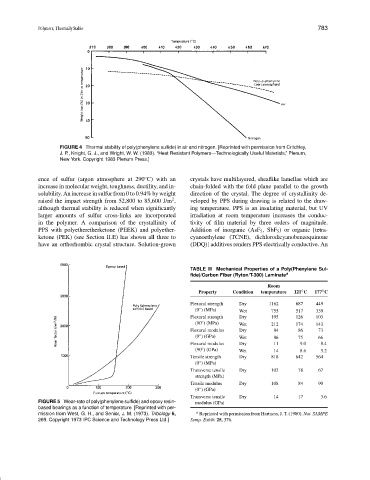
FIGURE 4 Thermal stability of poly(phenylene sulfide) in air and nitrogen. [Reprinted with permission from Critchley,
J. P., Knight, G. J., and Wright, W. W. (1983). “Heat Resistant Polymers—Technologically Useful Materials,” Plenum,
New York. Copyright 1983 Plenum Press.]
ence of sulfur (argon atmosphere at 290 C) with an crystals have multilayered, sheaflike lamellae which are
◦
increase in molecular weight, toughness, ductility, and in- chain-folded with the fold plane parallel to the growth
solubility. An increase in sulfur from 0 to 0.94% by weight direction of the crystal. The degree of crystallinity de-
2
raised the impact strength from 52,800 to 85,600 J/m , veloped by PPS during drawing is related to the draw-
although thermal stability is reduced when significantly ing temperature. PPS is an insulating material, but UV
larger amounts of sulfur cross-links are incorporated irradiation at room temperature increases the conduc-
in the polymer. A comparison of the crystallinity of tivity of film material by three orders of magnitude.
PPS with polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and polyether- Addition of inorganic (AsF 5 , SbF 5 ) or organic [tetra-
ketone (PEK) (see Section II.E) has shown all three to cyanoethylene (TCNE), dichlorodicyanobenzoquinone
have an orthorhombic crystal structure. Solution-grown (DDQ)] additives renders PPS electrically conductive. An
TABLE III Mechanical Properties of a Poly(Phenylene Sul-
fide)/Carbon Fiber (Ryton/T-300) Laminate a
Room
◦
◦
Property Condition temperature 121 C 177 C
Flexural strength Dry 1162 687 449
(0 ) (MPa) Wet 755 517 339
◦
Flexural strength Dry 195 126 103
◦
(90 ) (MPa) Wet 212 174 143
Flexural modulus Dry 84 86 73
(0 ) (GPa) Wet 86 75 66
◦
Flexural modulus Dry 11 9.0 8.4
(90 ) (GPa) Wet 14 8.6 5.2
◦
Tensile strength Dry 818 642 564
◦
(0 ) (MPa)
Transverse tensile Dry 103 78 67
strength (MPa)
Tensile modulus Dry 108 84 90
◦
(0 ) (GPa)
Transverse tensile Dry 14 17 3.6
FIGURE 5 Wear-rate of poly(phenylene sulfide) and epoxy resin- modulus (GPa)
based bearings as a function of temperature. [Reprinted with per-
mission from West, G. H., and Senior, J. M. (1973). Tribology 6, a Reprinted with permission from Hartness, J. T. (1980). Nat. SAMPE
269. Copyright 1973 IPC Science and Technology Press Ltd.] Symp. Exhib. 25, 376.