Page 276 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 276
P1: GPQ Final Pages/GNB P2: GTV
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En012c-604 July 26, 2001 16:2
Polymers, Thermally Stable 785
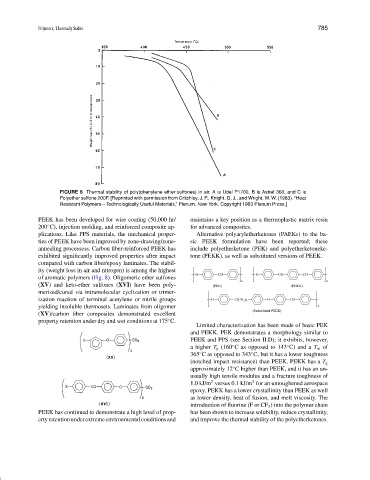
FIGURE 6 Thermal stability of poly(phenylene ether sulfones) in air. A is Udel P1700, B is Astrel 360, and C is
Polyether sulfone 200P. [Reprinted with permission from Critchley, J. P., Knight, G. J., and Wright, W. W. (1983). “Heat
Resistant Polymers—Technologically Useful Materials,” Plenum, New York. Copyright 1983 Plenum Press.]
PEEK has been developed for wire coating (50,000 hr/ maintains a key position as a thermoplastic matrix resin
200 C), injection molding, and reinforced composite ap- for advanced composites.
◦
plications. Like PPS materials, the mechanical proper- Alternative polyaryletherketones (PAEKs) to the ba-
ties of PEEK have been improved by zone-drawing/zone- sic PEEK formulation have been reported; these
annealing processess. Carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK has include polyetherketone (PEK) and polyetherketoneke-
exhibited significantly improved properties after impact tone (PEKK), as well as substituted versions of PEEK.
compared with carbon fiber/epoxy laminates. The stabil-
ity (weight loss in air and nitrogen) is among the highest
O CO O CO CO
of aromatic polymers (Fig. 8). Oligomeric ether sulfones
n n
(XV) and keto-ether sulfones (XVI) have been poly- (PEK) (PEKK)
merized/cured via intramolecular cyclization or trimer-
ization reaction of terminal acetylene or nitrile groups O C(CH 3 ) 2 O CO
yielding insoluble thermosets. Laminates from oligomer n
(Substituted PEEK)
(XV)/carbon fiber composites demonstrated excellent
◦
property retention under dry and wet conditions at 175 C.
Limited characterization has been made of basic PEK
and PEKK. PEK demonstrates a morphology similar to
PEEK and PPS (see Section II.D); it exhibits, however,
◦
a higher T g (160 C as opposed to 143 C) and a T m of
◦
365 C as opposed to 343 C, but it has a lower toughness
◦
◦
(notched impact resistance) than PEEK. PEKK has a T g
◦
approximately 12 C higher than PEEK, and it has an un-
usually high tensile modulus and a fracture toughness of
2
2
1.0 kJ/m versus 0.1 kJ/m for an untoughened aerospace
epoxy. PEKK has a lower crystallinity than PEEK as well
as lower density, heat of fusion, and melt viscosity. The
introduction of fluorine (F or CF 3 ) into the polymer chain
PEEK has continued to demonstrate a high level of prop- has been shown to increase solubility, reduce crystallinity,
ertyretentionunderextremeenvironmentalconditionsand and improve the thermal stability of the polyetherketones.