Page 283 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 283
P1: GPQ Final Pages/GNB P2: GTV
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En012c-604 July 26, 2001 16:2
792 Polymers, Thermally Stable
2. Polybenzazoles—Ordered Polymers
Highly ordered (rodlike) polymers derived from wholly
para-linked polybenzazoles (XXVI) have been developed
primarily as high-temperature fibers and self-reinforcing
resins.
Typically, PBO (XXVI,X = O) was originally developed
as a fiber by the Stanford Research Institute. It is now
R
marketed as Zylon by Dow Chemical, Co. who, in con-
junction with the Toyobo Research Center (Japan), have
devised a unique spinning technology to produce fiber
with a tenacity >5.8GPa.
Polybenzothiazoles (PBT) and polybenzoxazoles
(PBO) have merited particular attention since, like the
ordered aromatic polyamides, they form liquid crystalline
solutions. They are prepared in polyphosphoric acid (PPA)
solution with very high intrinsic viscosities ∼30 dL/g. The
spinning of the liquid crystalline solutions provides fibers
of exceptional stiffness and strength. Typical of the het-
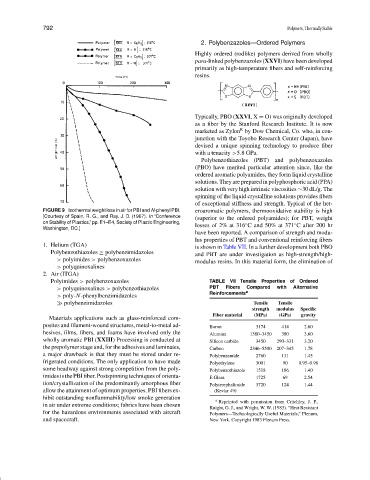
FIGURE 9 Isothermal weight loss in air for PBI and N-phenyl PBI. eroaromatic polymers, thermooxidative stability is high
[Courtesy of Spain, R. G., and Ray, J. D. (1967). In “Conference
(superior to the ordered polyamides); for PBT, weight
on Stability of Plastics,” pp. E1–E4, Society of Plastic Engineering,
losses of 2% at 316 C and 50% at 371 C after 200 hr
◦
◦
Washington, DC.]
have been reported. A comparison of strength and modu-
lus properties of PBT and conventional reinforcing fibers
1. Helium (TGA)
is shown in Table VII. In a further development both PBO
Polybenzothiazoles ≥ polybenzimidazoles
and PBT are under investigation as high-strength/high-
> polyimides > polybenzoxazoles
modulus resins. In this material form, the elimination of
> polyquinoxalines
2. Air (ITGA)
Polyimides > polybenzoxazoles TABLE VII Tensile Properties of Ordered
> polyquinoxalines > polybenzothiazoles PBT Fibers Compared with Alternative
Reinforcements a
> poly-N-phenylbenzimidazoles
polybenzimidazoles Tensile Tensile
strength modulus Specific
Fiber material (MPa) (GPa) gravity
Materials applications such as glass-reinforced com-
posites and filament-wound structures, metal-to-metal ad- Boron 3174 414 2.60
hesives, films, fibers, and foams have involved only the Alumina 1380–3450 380 3.60
wholly aromatic PBI (XXIII) Processing is conducted at Silicon carbide 3450 290–331 3.20
the prepolymer stage and, for the adhesives and laminates, Carbon 2346–5500 207–345 1.78
a major drawback is that they must be stored under re- Polybenzamide 2760 131 1.45
frigerated conditions. The only application to have made Polyethylene 3001 90 0.95–0.98
some headway against strong competition from the poly- Polybenzothiazole 1518 186 1.40
imides is the PBI fiber. Postspinning techniques of orienta- E Glass 1725 69 2.54
tion/crystallization of the predominantly amorphous fiber Polyterephalimide 3720 124 1.44
allow the attainment of optimum properties. PBI fibers ex- (Kevlar 49)
hibit outstanding nonflammability/low smoke generation
a Reprinted with permission from Critchley, J. P.,
in air under extreme conditions; fabrics have been chosen
Knight, G. J., and Wright, W. W. (1983). “Heat Resistant
for the hazardous environments associated with aircraft Polymers—Technologically Useful Materials,” Plenum,
and spacecraft. New York. Copyright 1983 Plenum Press.