Page 285 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 285
P1: GPQ Final Pages/GNB P2: GTV
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En012c-604 July 26, 2001 16:2
794 Polymers, Thermally Stable
Other potential cross-link sites have been introduced cial advances, particularly in the field of advanced com-
into the rigid-rod (PBT/PBO) molecules. These include posites. However, in the 1990s there was renewed interest
methyl, halogen, ethynyl, phenylene sulfide, and cy- in the synthesis, structure, and commercial potential of the
clobutene (BCB) moieties. The cyclobutene derivatives condensation-type polymers.
are reported to cross-link via quinone methide intermedi-
ates, which then undergo cycloaddition or dimerization
a. Condensation polyimides. Wholly aromatic
reactions. In the case of the PBT/BCB system, phase
polyimides (XXXIII) are almost invariably insoluble and
separation occurred between rigid-rod and matrix com-
infusible; as a result while strictly not cross-linked, at least
ponents and the desired synergystic effects were not re-
as prepared, they are referred to as “thermoset types.” Syn-
alized. However, with the PBO/BCB system, there was
thesis involves the low-temperature polycondensation (in
no phase separation after heat treatment and this resulted
dipolar aprotic solvents) of a dianhydride and diamine
in excellent tensile properties and improved resistance to
to produce a soluble/fusible intermediate poly(amic acid)
delamination.
followed by a chemically or, preferentially, thermally in-
In a novel approach, bulk rigid-rod molecular compos-
duced postpolymerization cyclization.
ites (XXXII) have been obtained by powder consolidation
of a copolymer with a PBT derivative as the backbone
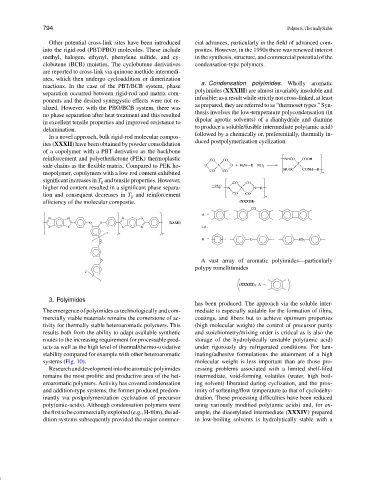
reinforcement and polyetherketone (PEK) thermoplastic CO CO NHCO COOH
side chains as the flexible matrix. Compared to PEK ho- O A O H 2 N R NH 2 A
CO CO HOOC CONH R
mopolymer, copolymers with a low rod content exhibited n
significant increases in T g and tensile properties. However, CO CO
higher rod content resulted in a significant phase separa- 2H 2 O N A N R
tion and consequent decreases in T g and reinforcement CO CO n
efficiency of the molecular composite. (XXXIII)
CO
A , ,
N N N S
O O (XXXII)
S S S N e.g.,
x y
R , O , SO 2
CO
A vast array of aromatic polyimides—particularly
O
polypy romellitimides
n
(XXXIII); A
3. Polyimides
has been produced. The approach via the soluble inter-
The emergence of polyimides as technologically and com- mediate is especially suitable for the formation of films,
mercially viable materials remains the cornerstone of ac- coatings, and fibers but to achieve optimum properties
tivity for thermally stable heteroaromatic polymers. This (high molecular weight) the control of precursor purity
results both from the ability to adapt available synthetic and stoichiometry/mixing order is critical as is also the
routes to the increasing requirement for processable prod- storage of the hydrolytically unstable poly(amic acid)
ucts as well as the high level of thermal/thermo-oxidative under rigorously dry refrigerated conditions. For lam-
stability compared for example with other heteroaromatic inating/adhesive formulations the attainment of a high
systems (Fig. 10). molecular weight is less important than are those pro-
Researchanddevelopmentintothearomaticpolyimides cessing problems associated with a limited shelf-lifed
remains the most prolific and productive area of the het- intermediate, void-forming volatiles (water, high boil-
eroaromatic polymers. Activity has covered condensation ing solvent) liberated during cyclization, and the prox-
and addition-type systems, the former produced predom- imity of softening/flow temperature to that of cyclodehy-
inantly via postpolymerization cyclization of precursor dration. These processing difficulties have been reduced
poly(amic-acids). Although condensation polymers were using variously modified poly(amic acids) and, for ex-
thefirsttobecommerciallyexploited(e.g.,H-film),thead- ample, the diacetylated intermediate (XXXIV) prepared
dition systems subsequently provided the major commer- in low-boiling solvents is hydrolytically stable with a