Page 296 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 296
P1: GPQ Final Pages/GNB P2: GTV
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En012c-604 July 26, 2001 16:2
Polymers, Thermally Stable 805
2. Poly(bisbenzimidazo-benzophenanthrolines)
Ladder LXIV and semiladder (LXV) polymers
are produced from the reaction of 1,4,5,8-naph-
thalenetetracarboxylic acid dianhydride and the appro-
priate tetraamine. Although a “staged” reaction via an
open-chain intermediate is possible, most frequently the
fully cyclized polymer is formed direct in PPA (150 C)
◦
or in the melt (300 C).
◦
For the semiladder system the introduction of flexible
groups [e.g., O and C(CF 3 ) 2 ] midchain has resulted
in an increased solubility and tractability. However, for
most practical applications, ladder system (LXIV) and
semiladder polymer (LXV;R = single bond), so called
BBL and BBB polymers, respectively, have been widely
evaluated. For BBB in particular, fiber spun from concen-
trated sulfuric acid exhibits excellent tensile properties
under ambient conditions and in air approximately 60%
◦
Applications such as films and fibers are formed at of initial tensile strength is retained after 30 hr at 360 Cor
◦
the “open-chain” stage with subsequent cyclization (250– 1 min at 600 C. Comparative strength retention at elevated
325 C) to the pyrrone. For both material forms optimum temperature for BBB, PBI, and Nomex is shown in Fig. 14.
◦
◦
performance is obtained from semiladder systems, for ex- However, the long-term strength of BBB at 360 Cisin-
ample,fibersfrompolymerLXIIIAr ,R=singlebond) ferior to a nonladder benzoxazole-imide copolymer fiber.
retain room temperature tensile properties after exposure Strong, high-modulus films of BBB and BBL polymers
(12 hr) to 10% NaOH at 90 C or air at 400 C. Solid grades have been formed by precipitation (from methane sulfonic
◦
◦
of ladder or semiladder homo- or heterocyclic (imide, acid solution) and vacuum filtration. It is suggested that a
benzimidazole, oxadiazole) copolymers have been pro- high degree of interchain packing is responsible for this
duced by high-temperature/high pressure molding pro- effect. Differences are observed for BBB and BBL poly-
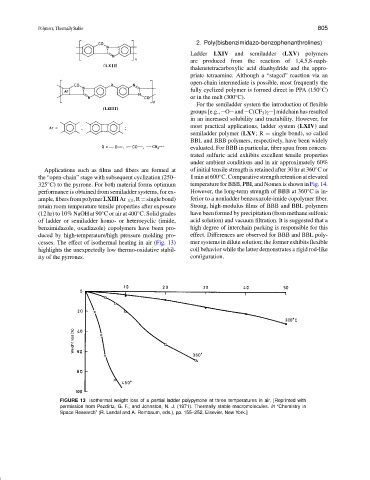
cesses. The effect of isothermal heating in air (Fig. 13) mer systems in dilute solution; the former exhibits flexible
highlights the unexpectedly low thermo-oxidative stabil- coil behavior while the latter demonstrates a rigid rod-like
ity of the pyrrones. configuration.
FIGURE 13 Isothermal weight loss of a partial ladder polypyrrone at three temperatures in air. [Reprinted with
permission from Pezdirtz, G. F., and Johnston, N. J. (1971). Thermally stable macromolecules. In “Chemistry in
Space Research” (R. Landal and A. Rembaum, eds.), pp. 155–252, Elsevier, New York.]