Page 295 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 295
P1: GPQ Final Pages/GNB P2: GTV
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En012c-604 July 26, 2001 16:2
804 Polymers, Thermally Stable
TABLE IX Properties of Polyquinoxaline/Boron and Carbon Composites
C-Fiber B-Fiber
Flexural Flexural
Test temperature strength Modulus ILSS a strength Modulus
◦
( C)/test condition (MPa) (GPa) MPa (MPa) (GPa)
RT 842 107 88 1746 292
133 1359 250
177 1384 259
212 1242 255
316 1524 167
316 after 1 hr/316 816 105 59
316 after 100 hr/316 802 104 58
316 after 200 hr/316 651 101 48
361 1666 83
371 after 1 hr/371 748 104 61
371 after 10 hr/371 713 100 61
a
Interlaminar shear strength.
tetracarboxylic dianhydride and aromatic tetramine, have
provided a range of structural materials that, though not
currently commercially developed, has demonstrated def-
inite potential in high-temperature applications.
1. Poly(benzimidazopyrrolones)—Pyrrones
Pyrrone polymers have been produced in full ladder
The majority of ladder systems are intractable “brick (LXII) or semiladder via soluble (LXIII) form via soluble
dusts” but two chemically related systems in partic- “open-chain” intermediates (cf. polyimides) or directly in
ular, produced from the interaction of an aromatic polyphosphoric acid solution.
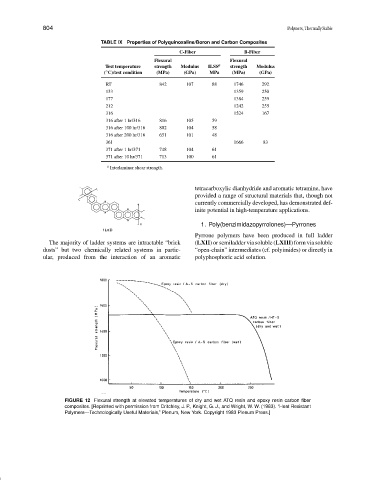
FIGURE 12 Flexural strength at elevated temperatures of dry and wet ATQ resin and epoxy resin carbon fiber
composites. [Reprinted with permission from Critchley, J. P., Knight, G. J., and Wright, W. W. (1983). “Heat Resistant
Polymers—Technologically Useful Materials,” Plenum, New York. Copyright 1983 Plenum Press.]