Page 31 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 31
P1: FPP 2nd Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-64 May 19, 2001 20:39
Biopolymers 235
form. In an RNA double helix, there are approximately
eleven base pairs per turn of the helix, and uracil, instead
of the thymine of DNA, base-pairs with adenine. The sin-
gle polynucleotide chains are folded to give short stretches
of double helix separated by single-stranded nonhelical
segments.
The secondary structures (helices) and tertiary struc-
tures (overall chain folding) of RNA are not uniform and
differ with the type of RNA. The chain folding is often
complex, involving short helices, loops, and even 3- or
4-wayjunctionsofsingle-strandedchain.MessengerRNA
molecules carry in their base sequences the information
specifying protein amino acid sequence. There is one mes-
senger for each protein, and so m-RNA molecules vary
greatly in length and sequence; hence they differ in sec-
ondary and tertiary structure. Ribosomal ribonucleic acids
form part of the structures known as ribosomes, where pro-
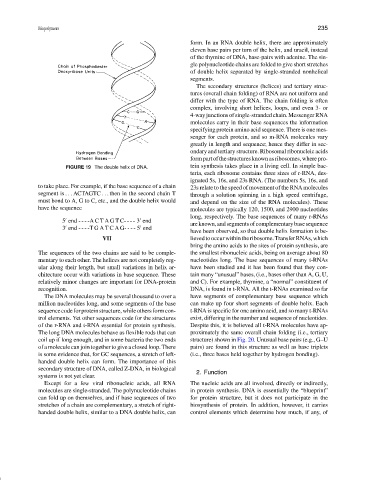
FIGURE 19 The double helix of DNA. tein synthesis takes place in a living cell. In simple bac-
teria, each ribosome contains three sizes of r-RNA, des-
ignated 5s, 16s, and 23s RNA. (The numbers 5s, 16s, and
to take place. For example, if the base sequence of a chain 23s relate to the speed of movement of the RNA molecules
segment is ... ACTAGTC ... then in the second chain T through a solution spinning in a high speed centrifuge,
must bond to A, G to C, etc., and the double helix would and depend on the size of the RNA molecules). These
have the sequence molecules are typically 120, 1500, and 2900 nucleotides
long, respectively. The base sequences of many r-RNAs
5 end ----ACTAGTC---- 3 end
areknown,andsegmentsofcomplementarybasesequence
3 end ----TGATCAG---- 5 end
have been observed, so that double helix formation is be-
VII lievedtooccurwithintheribosome.TransferRNAs,which
bring the amino acids to the sites of protein synthesis, are
The sequences of the two chains are said to be comple- the smallest ribonucleic acids, being on average about 80
mentary to each other. The helices are not completely reg- nucleotides long. The base sequences of many t-RNAs
ular along their length, but small variations in helix ar- have been studied and it has been found that they con-
chitecture occur with variations in base sequence. These tain many “unusual” bases, (i.e., bases other than A, G, U,
relatively minor changes are important for DNA-protein and C). For example, thymine, a “normal” constituent of
recognition. DNA, is found in t-RNA. All the t-RNAs examined so far
The DNA molecules may be several thousand to over a have segments of complementary base sequence which
million nucleotides long, and some segments of the base can make up four short segments of double helix. Each
sequencecodeforproteinstructure,whileothersformcon- t-RNA is specific for one amino acid, and so many t-RNAs
trol elements. Yet other sequences code for the structures exist, differing in the number and sequence of nucleotides.
of the r-RNA and t-RNA essential for protein synthesis. Despite this, it is believed all t-RNA molecules have ap-
The long DNA molecules behave as flexible rods that can proximately the same overall chain folding (i.e., tertiary
coil up if long enough, and in some bacteria the two ends structure) shown in Fig. 20. Unusual base pairs (e.g., G–U
of a molecule can join together to give a closed loop. There pairs) are found in this structure as well as base triplets
is some evidence that, for GC sequences, a stretch of left- (i.e., three bases held together by hydrogen bonding).
handed double helix can form. The importance of this
secondary structure of DNA, called Z-DNA, in biological
2. Function
systems is not yet clear.
Except for a few viral ribonucleic acids, all RNA The nucleic acids are all involved, directly or indirectly,
molecules are single-stranded. The polynucleotide chains in protein synthesis. DNA is essentially the “blueprint”
can fold up on themselves, and if base sequences of two for protein structure, but it does not participate in the
stretches of a chain are complementary, a stretch of right- biosynthesis of protein. In addition, however, it carries
handed double helix, similar to a DNA double helix, can control elements which determine how much, if any, of