Page 322 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 322
P1: GQQ/GLT P2: GRB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN014B-670 July 28, 2001 16:50
388 Rubber, Natural
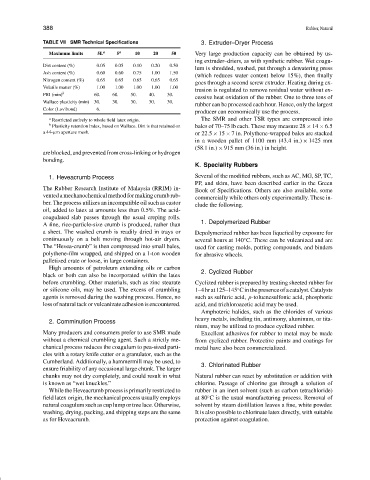
TABLE VII SMR Technical Specifications 3. Extruder–Dryer Process
Maximum limits 5L a 5 a 10 20 50 Very large production capacity can be obtained by us-
ing extruder–driers, as with synthetic rubber. Wet coagu-
Dirt content (%) 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.20 0.50
lum is shredded, washed, put through a dewatering press
Ash content (%) 0.60 0.60 0.75 1.00 1.50
(which reduces water content below 15%), then finally
Nitrogen content (%) 0.65 0.65 0.65 0.65 0.65
goes through a second screw extruder. Heating during ex-
Volatile matter (%) 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 trusion is regulated to remove residual water without ex-
PRI (min) b 60. 60. 50. 40. 30.
cessive heat oxidation of the rubber. One to three tons of
Wallace plasticity (min) 30. 30. 30. 30. 30.
rubber can be processed each hour. Hence, only the largest
Color (Lovibond) 6. — — — —
producer can economically use the process.
a Restricted entirely to whole field latex origin. The SMR and other TSR types are compressed into
b Plasticity retention index, based on Wallace. Dirt is that retained on bales of 70–75 lb each. These may measure 28 × 14 × 6.5
a 44-µm aperture mesh. or 22.5 × 15 × 7 in. Polythene-wrapped bales are stacked
in a wooden pallet of 1100 mm (43.4 in.) × 1425 mm
(58.1 in.) × 915 mm (36 in.) in height.
are blocked, and prevented from cross-linking or hydrogen
bonding.
K. Speciality Rubbers
1. Heveacrumb Process Several of the modified rubbers, such as AC, MG, SP, TC,
PP, and skim, have been described earlier in the Green
The Rubber Research Institute of Malaysia (RRIM) in- Book of Specifications. Others are also available, some
vented a mechanochemical method for making crumb rub- commercially while others only experimentally. These in-
ber. The process utilizes an incompatible oil such as castor clude the following.
oil, added to latex at amounts less than 0.5%. The acid-
coagulated slab passes through the usual creping rolls.
1. Depolymerized Rubber
A fine, rice-particle-size crumb is produced, rather than
a sheet. The washed crumb is readily dried in trays or Depolymerized rubber has been liquefied by exposure for
continuously on a belt moving through hot-air dryers. several hours at 140 C. These can be vulcanized and are
◦
The “Hevea-crumb” is then compressed into small bales, used for casting molds, potting compounds, and binders
polythene-film wrapped, and shipped on a 1-ton wooden for abrasive wheels.
palletized crate or loose, in large containers.
High amounts of petroleum extending oils or carbon
black or both can also be incorporated within the latex 2. Cyclized Rubber
before crumbling. Other materials, such as zinc stearate Cyclized rubber is prepared by treating sheeted rubber for
or silicone oils, may be used. The excess of crumbling 1–4hrat125–145 Cinthepresenceofacatalyst.Catalysts
◦
agents is removed during the washing process. Hence, no such as sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, phosphoric
loss of natural tack or vulcanizate adhesion is encountered. acid, and trichloroacetic acid may be used.
Amphoteric halides, such as the chlorides of various
heavy metals, including tin, antimony, aluminum, or tita-
2. Comminution Process
nium, may be utilized to produce cyclized rubber.
Many producers and consumers prefer to use SMR made Excellent adhesives for rubber to metal may be made
without a chemical crumbling agent. Such a strictly me- from cyclized rubber. Protective paints and coatings for
chanical process reduces the coagulum to pea-sized parti- metal have also been commercialized.
cles with a rotary knife cutter or a granulator, such as the
Cumberland. Additionally, a hammermill may be used, to 3. Chlorinated Rubber
ensure friability of any occasional large chunk. The larger
chunks may not dry completely, and could result in what Natural rubber can react by substitution or addition with
is known as “wet knuckles.” chlorine. Passage of chlorine gas through a solution of
While the Heveacrumb process is primarily restricted to rubber in an inert solvent (such as carbon tetrachloride)
field latex origin, the mechanical process usually employs at 80 C is the usual manufacturing process. Removal of
◦
natural coagulum such as cup lump or tree lace. Otherwise, solvent by steam distillation leaves a fine, white powder.
washing, drying, packing, and shipping steps are the same It is also possible to chlorinate latex directly, with suitable
as for Heveacrumb. protection against coagulation.