Page 39 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 39
P1: FPP 2nd Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-64 May 19, 2001 20:39
Biopolymers 243
and rubber gloves. With high (30–50%) sulfur content, structure without degrading the molecules. It is believed
rubber is not elastic, but forms a hard, rigid substance that the monomers are alcohols like XI, where X may be
called ebonite which can be used as a thermal and electric H or OCH 3 . The content of OCH 3 groups in the lignin
insulator. depends on the plant source.
The double bonds in rubber molecules are fairly readily
oxidized; when this happens the rubber becomes less elas- X
tic.Thusantioxidantssuchasphenyl-α-naphthylamineare
usually incorporated into a vulcanizing mixture. HO CH CH CH 2 OH
Vulcanized rubber does not have high abrasion resis-
tance, but this property can be improved by incorporat- X
ing a filler before vulcanization. The most common filler
is carbon black (soot) and this forms loose bonds to the XI
rubber molecules. The result is a reinforced rubber with
2
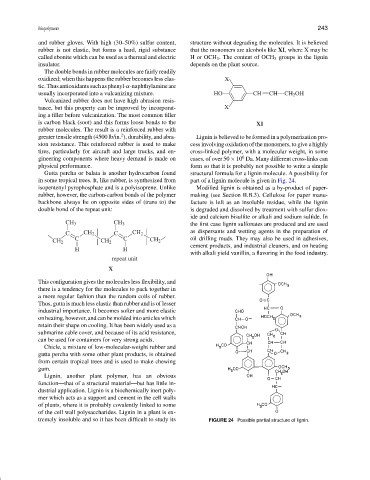
greater tensile strength (4500 lb/in. ), durability, and abra- Lignin is believed to be formed in a polymerization pro-
sion resistance. This reinforced rubber is used to make cess involving oxidation of the monomers, to give a highly
tires, particularly for aircraft and large trucks, and en- cross-linked polymer, with a molecular weight, in some
6
gineering components where heavy demand is made on cases, of over 50 × 10 Da. Many different cross-links can
physical performance. form so that it is probably not possible to write a simple
Gutta percha or balata is another hydrocarbon found structural formula for a lignin molecule. A possibility for
in some tropical trees. It, like rubber, is synthesized from part of a lignin molecule is given in Fig. 24.
isopentenyl pyrophosphate and is a polyisoprene. Unlike Modified lignin is obtained as a by-product of paper-
rubber, however, the carbon-carbon bonds of the polymer making (see Section II.B.3). Cellulose for paper manu-
backbone always lie on opposite sides of (trans to) the facture is left as an insoluble residue, while the lignin
double bond of the repeat unit: is degraded and dissolved by treatment with sulfur diox-
ide and calcium bisulfite or alkali and sodium sulfide. In
CH 3 CH 3 the first case lignin sulfonates are produced and are used
C CH 2 C CH 2 as dispersants and wetting agents in the preparation of
C C oil drilling muds. They may also be used in adhesives,
CH 2 CH 2 CH 2
cement products, and industrial cleaners, and on heating
H H
with alkali yield vanillin, a flavoring in the food industry.
repeat unit
X
This configuration gives the molecules less flexibility, and
there is a tendency for the molecules to pack together in
a more regular fashion than the random coils of rubber.
Thus, gutta is much less elastic than rubber and is of lesser
industrial importance. It becomes softer and more elastic
onheating,however, and can be molded into articleswhich
retain their shape on cooling. It has been widely used as a
submarine cable cover, and because of its acid resistance,
can be used for containers for very strong acids.
Chicle, a mixture of low-molecular-weight rubber and
gutta percha with some other plant products, is obtained
from certain tropical trees and is used to make chewing
gum.
Lignin, another plant polymer, has an obvious
function—that of a structural material—but has little in-
dustrial application. Lignin is a biochemically inert poly-
mer which acts as a support and cement in the cell walls
of plants, where it is probably covalently linked to some
of the cell wall polysaccharides. Lignin in a plant is ex-
tremely insoluble and so it has been difficult to study its FIGURE 24 Possible partial structure of lignin.