Page 123 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 123
P1: GLM Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007C-307 June 29, 2001 19:40
200 Halogen Chemistry
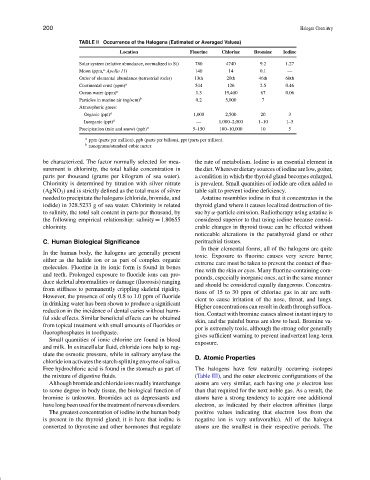
TABLE II Occurrence of the Halogens (Estimated or Averaged Values)
Location Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine
Solar system (relative abundance, normalized to Si) 780 4740 9.2 1.27
a
Moon (ppm, Apollo 11) 140 14 0.1 —
Order of elemental abundance (terrestrial rocks) 13th 20th 46th 60th
Continental crust (ppm) a 544 126 2.5 0.46
Ocean water (ppm) a 1.3 19,400 67 0.06
Particles in marine air (ng/scm) b 0.2 5,000 7
Atmospheric gases:
Organic (ppt) a 1,000 2,500 20 3
Inorganic (ppt) a — 1,000–2,000 1–10 1–5
Precipitation (rain and snow) (ppb) a 5–150 100–10,000 10 5
a
ppm (parts per million), ppb (parts per billion), ppt (parts per trillion).
b
nanograms/standard cubic meter.
be characterized. The factor normally selected for mea- the rate of metabolism. Iodine is an essential element in
surement is chlorinity, the total halide concentration in the diet. Wherever dietary sources of iodine are low, goiter,
parts per thousand (grams per kilogram of sea water). a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes enlarged,
Chlorinity is determined by titration with silver nitrate is prevalent. Small quantities of iodide are often added to
(AgNO 3 ) and is strictly defined as the total mass of silver table salt to prevent iodine deficiency.
needed to precipitate the halogens (chloride, bromide, and Astatine resembles iodine in that it concentrates in the
iodide) in 328.5233 g of sea water. Chlorinity is related thyroid gland where it causes localized destruction of tis-
to salinity, the total salt content in parts per thousand, by sue by α-particle emission. Radiotherapy using astatine is
the following empirical relationship: salinity = 1.80655 considered superior to that using iodine because consid-
chlorinity. erable changes in thyroid tissue can be effected without
noticeable alterations in the parathyroid gland or other
C. Human Biological Significance peritrachial tissues.
In their elemental forms, all of the halogens are quite
In the human body, the halogens are generally present
toxic. Exposure to fluorine causes very severe burns;
either as the halide ion or as part of complex organic
extreme care must be taken to prevent the contact of fluo-
molecules. Fluorine in its ionic form is found in bones
rine with the skin or eyes. Many fluorine-containing com-
and teeth. Prolonged exposure to fluoride ions can pro-
pounds, especially inorganic ones, act in the same manner
duce skeletal abnormalities or damage (fluorosis) ranging
and should be considered equally dangerous. Concentra-
from stiffness to permanently crippling skeletal rigidity.
tions of 15 to 30 ppm of chlorine gas in air are suffi-
However, the presence of only 0.8 to 1.0 ppm of fluoride
cient to cause irritation of the nose, throat, and lungs.
in drinking water has been shown to produce a significant
Higher concentrations can result in death through suffoca-
reduction in the incidence of dental caries without harm-
tion. Contact with bromine causes almost instant injury to
ful side effects. Similar beneficial effects can be obtained
skin, and the painful burns are slow to heal. Bromine va-
from topical treatment with small amounts of fluorides or
por is extremely toxic, although the strong odor generally
fluorophosphates in toothpaste.
gives sufficient warning to prevent inadvertent long-term
Small quantities of ionic chlorine are found in blood
exposure.
and milk. In extracellular fluid, chloride ions help to reg-
ulate the osmotic pressure, while in salivary amylase the D. Atomic Properties
chloride ion activates the starch-splitting enzyme of saliva.
Free hydrochloric acid is found in the stomach as part of The halogens have few naturally occurring isotopes
the mixture of digestive fluids. (Table III), and the outer electronic configurations of the
Althoughbromideandchlorideionsreadilyinterchange atoms are very similar, each having one p electron less
to some degree in body tissue, the biological function of than that required for the next noble gas. As a result, the
bromine is unknown. Bromides act as depressants and atoms have a strong tendency to acquire one additional
have long been used for the treatment of nervous disorders. electron, as indicated by their electron affinities (large
The greatest concentration of iodine in the human body positive values indicating that electron loss from the
is present in the thyroid gland; it is here that iodine is negative ion is very unfavorable). All of the halogen
converted to thyroxine and other hormones that regulate atoms are the smallest in their respective periods. The