Page 170 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 170
P1: GPA Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007D-343 July 10, 2001 20:13
828 Inorganic Exotic Molecules
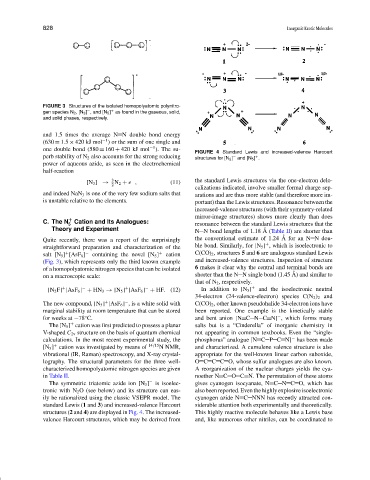
FIGURE 3 Structures of the isolated homopolyatomic polynitro-
−
+
gen species N 2 ,[N 3 ] , and [N 5 ] as found in the gaseous, solid,
and solid phases, respectively.
and 1.5 times the average N N double bond energy
−1
(630 = 1.5 × 420 kJ mol ) or the sum of one single and
−1
one double bond (580 = 160 + 420 kJ mol ). The su-
FIGURE 4 Standard Lewis and increased-valence Harcourt
perb stability of N 2 also accounts for the strong reducing structures for [N 3 ] and [N 5 ] .
−
+
power of aqueous azide, as seen in the electrochemical
half-reaction
3
−
−
[N 3 ] → N 2 + e , (11) the standard Lewis structures via the one-electron delo-
2
calizations indicated, involve smaller formal charge sep-
and indeed NaN 3 is one of the very few sodium salts that arations and are thus more stable (and therefore more im-
is unstable relative to the elements. portant) than the Lewis structures. Resonance between the
increased-valence structures (with their symmetry-related
mirror-image structures) shows more clearly than does
+ ++
C. The N Cation and Its Analogues:
5 resonance between the standard Lewis structures that the
Theory and Experiment N N bond lengths of 1.18 A (Table II) are shorter than
˚
˚
Quite recently, there was a report of the surprisingly the conventional estimate of 1.24 A for an N N dou-
+
straightforward preparation and characterization of the ble bond. Similarly, for [N 5 ] , which is isoelectronic to
salt [N 5 ] [AsF 6 ] − containing the novel [N 5 ] + cation C(CO) 2 , structures 5 and 6 are analogous standard Lewis
+
(Fig. 3), which represents only the third known example and increased-valence structures. Inspection of structure
of a homopolyatomic nitrogen species that can be isolated 6 makes it clear why the central and terminal bonds are
˚
on a macroscopic scale: shorter than the N N single bond (1.45 A) and similar to
that of N 2 , respectively.
+
[N 2 F] [AsF 6 ] + HN 3 → [N 5 ] [AsF 6 ] + HF. (12) In addition to [N 5 ] + and the isoelectronic neutral
−
+
−
34-electron (24-valence-electron) species C(N 2 ) 2 and
+
−
The new compound, [N 5 ] [AsF 6 ] , is a white solid with C(CO) 2 , other known pseudohalide 34-electron ions have
marginal stability at room temperature that can be stored been reported. One example is the kinetically stable
−
for weeks at −78 C. and bent anion [N C N C N] , which forms many
◦
The [N 5 ] cation was first predicted to possess a planar salts but is a “Cinderella” of inorganic chemistry in
+
V-shaped C 2v structure on the basis of quantum chemical not appearing in common textbooks. Even the “single-
calculations. In the most recent experimental study, the phosphorus” analogue [N C P C N] has been made
−
[N 5 ] cation was investigated by means of 14/15 N NMR, and characterized. A cumulene valence structure is also
+
vibrational (IR, Raman) spectroscopy, and X-ray crystal- appropriate for the well-known linear carbon suboxide,
lography. The structural parameters for the three well- O C C C O, whose sulfur analogues are also known.
characterized homopolyatomic nitrogen species are given A reorganization of the nuclear charges yields the cya-
in Table II. noether N C O C N. The permutation of these atoms
The symmetric triatomic azide ion [N 3 ] − is isoelec- gives cyanogen isocyanate, N C N C O, which has
tronic with N 2 O (see below) and its structure can eas- alsobeenreported.Eventhehighlyexplosiveisoelectronic
ily be rationalized using the classic VSEPR model. The cyanogen azide N C NNN has recently attracted con-
standard Lewis (1 and 3) and increased-valence Harcourt siderable attention both experimentally and theoretically.
structures (2 and 4) are displayed in Fig. 4. The increased- This highly reactive molecule behaves like a Lewis base
valence Harcourt structures, which may be derived from and, like numerous other nitriles, can be coordinated to