Page 171 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 171
P1: GPA Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007D-343 July 10, 2001 20:13
Inorganic Exotic Molecules 829
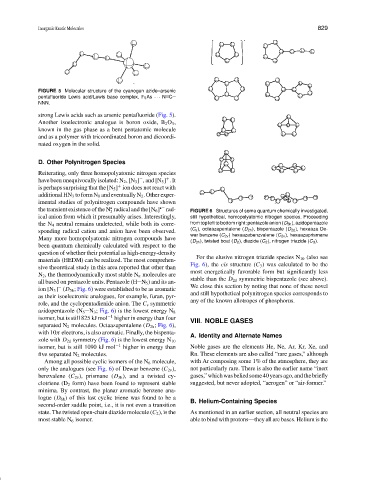
FIGURE 5 Molecular structure of the cyanogen azide–arsenic
pentafluoride Lewis acid/Lewis base complex, F 5 As ··· N C
NNN.
strong Lewis acids such as arsenic pentafluoride (Fig. 5).
Another isoelectronic analogue is boron oxide, B 2 O 3 ,
known in the gas phase as a bent pentatomic molecule
and as a polymer with tricoordinated boron and dicoordi-
nated oxygen in the solid.
D. Other Polynitrogen Species
Reiterating, only three homopolyatomic nitrogen species
−
+
have been unequivocally isolated: N 2 ,[N 3 ] , and [N 5 ] .It
+
is perhaps surprising that the [N 5 ] ion does not react with
additional HN 3 to form N 8 and eventually N 2 . Other exper-
imental studies of polynitrogen compounds have shown
•
the transient existence of the N radical and the [N 6 ] •− rad-
3 FIGURE 6 Structures of some quantum chemically investigated,
ical anion from which it presumably arises. Interestingly, still hypothetical, homopolyatomic nitrogen species. Proceeding
the N 4 neutral remains undetected, while both its corre- from top left to bottom right: pentazole anion (D 5h ), azidopentazole
sponding radical cation and anion have been observed. (C s ), octaazapentalene (D 2h ), bispentazole (D 2d ), hexaaza De-
war benzene (C 2v ) hexaazabenzvalene (C 2v ), hexaazaprismane
Many more homopolyatomic nitrogen compounds have
(D 3h ), twisted boat (D 2 ), diazide (C 2 ), nitrogen triazide (C 3 ).
been quantum chemically calculated with respect to the
question of whether their potential as high-energy-density
For the elusive nitrogen triazide species N 10 (also see
materials (HEDM) can be realized. The most comprehen-
Fig. 6), the cis structure (C 3 ) was calculated to be the
sive theoretical study in this area reported that other than
most energetically favorable form but significantly less
N 2 , the thermodynamically most stable N n molecules are
stable than the D 2d symmetric bispentazole (see above).
all based on pentazole units. Pentazole (H N 5 ) and its an-
− We close this section by noting that none of these novel
ion [N 5 ] (D 5h ; Fig. 6) were established to be as aromatic
and still hypothetical polynitrogen species corresponds to
as their isoelectronic analogues, for example, furan, pyr-
any of the known allotropes of phosphorus.
role, and the cyclopentadienide anion. The C s symmetric
azidopentazole (N 5 N 3 ; Fig. 6) is the lowest energy N 8
isomer, but is still 825 kJ mol −1 higher in energy than four VIII. NOBLE GASES
separated N 2 molecules. Octaazapentalene (D 2h ; Fig. 6),
with 10π electrons, is also aromatic. Finally, the bispenta-
A. Identity and Alternate Names
zole with D 2d symmetry (Fig. 6) is the lowest energy N 10
isomer, but is still 1090 kJ mol −1 higher in energy than Noble gases are the elements He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and
five separated N 2 molecules. Rn. These elements are also called “rare gases,” although
Among all possible cyclic isomers of the N 6 molecule, with Ar composing some 1% of the atmosphere, they are
only the analogues (see Fig. 6) of Dewar benzene (C 2v ), not particularly rare. There is also the earlier name “inert
benzvalene (C 2v ), prismane (D 3h ), and a twisted cy- gases,”whichwasbeliedsome40yearsago,andthebriefly
clotriene (D 2 form) have been found to represent stable suggested, but never adopted, “aerogen” or “air-former.”
minima. By contrast, the planar aromatic benzene ana-
logue (D 6h ) of this last cyclic triene was found to be a
B. Helium-Containing Species
second-order saddle point, i.e., it is not even a transition
state. The twisted open-chain diazide molecule (C 2 ), is the As mentioned in an earlier section, all neutral species are
most stable N 6 isomer. able to bind with protons—they all are bases. Helium is the