Page 84 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 84
P1: FQP/LPB P2: FQP Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN003D-147 June 13, 2001 22:58
Coordination Compounds 755
2+ TABLE IX Properties of Cis and Trans Isomers of Square
−
such as [BeF 4 ] , [AlCl 4 ] , and [Zn(NH 3 ) 4 ] are com-
2−
[PtA 2 B 2 ]
mon. For the first transition series, they are quite common
among anions and with very polarizable ligands, as in Geometry
2−
the blue ion [CoBr 4 ] and in the blue β form (so-called A B Isomer µ a Other properties
for historical reasons: names used to distinguish poly-
morphic varieties are unsystematic) of [Co(C 5 H 5 N) 2 Cl 2 ]. NH 3 Cl Cis — H 2 SO 4 → adduct
There is another form of this dimorphic compound, the Drug
pink α, which is polymeric in the crystal (through chlo- NH 3 Cl Trans — H 2 SO 4 → no adduct
rine bridging two cobalt ions) and contains octahedral Not drug
cobalt(II) ions. The very highly polarizing ions of the P(C 2 H 5 ) 3 Cl Cis 10.6 White
highest oxidation states of the central transition elements P(C 2 H 5 ) 3 Cl Trans 0 Yellow
often have essentially tetrahedral shapes. Some exam- a Dipole moment (in debye units).
3−
2−
ples are VO , CrO , MnO − these being an isoelec-
4 4 4
−
2−
tronic set; MnO ; FeO 2− (so-called ferrate); [CrO 3 Cl] ,
4 4
[TcO 4 ] , [ReO 4 ] , [OsO 4 N] − (osmiamate); and many The subtlety of metal complex chemistry is manifest in
−
−
others. the apparently similar bisglycinatocopper(II) system, the
The planar four-coordinated molecules are of great behavior of which is actually opposite to that of alaninate:
rarity in main group chemistry (ICl , XeF 4 ) but dom- The initial aqueous solution gives first the metastable
−
4
inate the simple coordination chemistry of spin-paired crystals of the cis isomer, which is slowly replaced by the
8
d species. These crop up among the second and third trans.
8
row platinum and coinage metals, and there are a few For the kinetically inert spin-paired d species, such
8
examples for (3d) , chiefly for nickel(II) with strong- as palladium(II) and platinum(II), this cis–trans (geo-
2−
2+
field (polarizable) ligands: [Ni(CN) 4 ] , [Pd(NH 3 ) 4 ] , metric) isomerism occurs frequently. Table IX shows
[Pt(NH 3 ) 2 Cl 2 ], [AuCl 4 ] . some examples. For such compositions as those in Ta-
−
ble IX, there is often another kind of isomerism (ion-
ization isomerism) in which the same stoichiometry Pt–
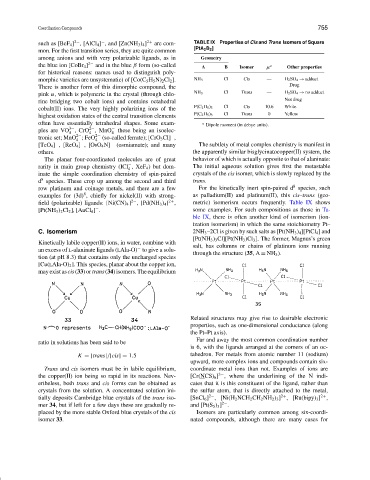
C. Isomerism 2NH 3 –2Cl is given by such salts as [Pt(NH 3 ) 4 ][PtCl 4 ] and
[Pt(NH 3 ) 3 Cl][Pt(NH 3 )Cl 3 ]. The former, Magnus’s green
Kinetically labile copper(II) ions, in water, combine with salt, has columns or chains of platinum ions running
−
an excess of L-alaninate ligands (LAla-O) to give a solu-
through the structure (35,A = NH 3 ).
tion (at pH 8.3) that contains only the uncharged species
[Cu(LAla-O) 2 ]. This species, planar about the copper ion,
mayexistascis(33)ortrans(34)isomers.Theequilibrium
Related structures may give rise to desirable electronic
properties, such as one-dimensional conductance (along
the Pt–Pt axis).
Far and away the most common coordination number
ratio in solutions has been said to be
is 6, with the ligands arranged at the corners of an oc-
K = [trans]/[cis] = 1.5 tahedron. For metals from atomic number 11 (sodium)
upward, more complex ions and compounds contain six-
Trans and cis isomers must be in labile equilibrium, coordinate metal ions than not. Examples of ions are
the copper(II) ion being so rapid in its reactions. Nev- [Cr(NCS) 6 ] , where the underlining of the N indi-
3−
ertheless, both trans and cis forms can be obtained as cates that it is this constituent of the ligand, rather than
crystals from the solution. A concentrated solution ini- the sulfur atom, that is directly attached to the metal,
tially deposits Cambridge blue crystals of the trans iso- [SnCl 6 ] , [Ni(H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2 ) 3 ] , [Ru(bipy) 3 ] ,
2+
2−
2+
mer 34, but if left for a few days these are gradually re- and [Pt(S 5 ) 3 ] .
2−
placed by the more stable Oxford blue crystals of the cis Isomers are particularly common among six-coordi-
isomer 33. nated compounds, although there are many cases for