Page 15 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Molecular Biology
P. 15
P1: GQQ Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-90 May 17, 2001 20:42
Cell Death (Apoptosis) 553
phosphatase, which is abundant in lysosomes, giving rise localized in the plasma membrane and the endoplasmic
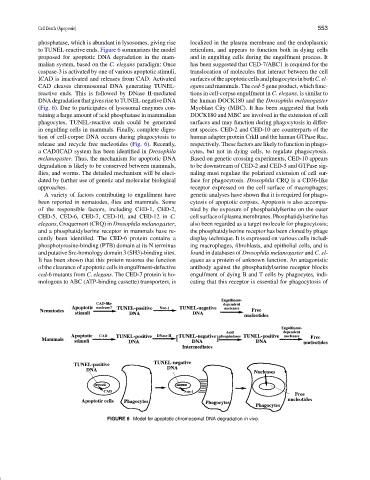
to TUNEL-reactive ends. Figure 6 summarizes the model reticulum, and appears to function both in dying cells
proposed for apoptotic DNA degradation in the mam- and in engulfing cells during the engulfment process. It
malian system, based on the C. elegans paradigm: Once has been suggested that CED-7/ABC1 is required for the
caspase-3 is activated by one of various apoptotic stimuli, translocation of molecules that interact between the cell
ICAD is inactivated and releases from CAD. Activated surfacesoftheapoptoticcellsandphagocytesinbothC.el-
CAD cleaves chromosomal DNA generating TUNEL- egans and mammals. The ced-5 gene product, which func-
reactive ends. This is followed by DNase II-mediated tions in cell-corpse engulfment in C. elegans, is similar to
DNA degradation that gives rise to TUNEL-negative DNA the human DOCK180 and the Drosophila melanogaster
(Fig. 6). Due to participates of lysosomal enzymes con- Myoblast City (MBC). It has been suggested that both
taining a large amount of acid phosphatase in mammalian DOCK180 and MBC are involved in the extension of cell
phagocytes, TUNEL-reactive ends could be generated surfaces and may function during phagocytosis in differ-
in engulfing cells in mammals. Finally, complete diges- ent species. CED-2 and CED-10 are counterparts of the
tion of cell-corpse DNA occurs during phagocytosis to human adapter protein CrkII and the human GTPase Rac,
release and recycle free nucleotides (Fig. 6). Recently, respectively. These factors are likely to function in phago-
a CAD/ICAD system has been identified in Drosophila cytes, but not in dying cells, to regulate phagocytosis.
melanogaster. Thus, the mechanism for apoptotic DNA Based on genetic crossing experiments, CED-10 appears
degradation is likely to be conserved between mammals, to be downstream of CED-2 and CED-5 and GTPase sig-
flies, and worms. The detailed mechanism will be eluci- naling must regulate the polarized extension of cell sur-
dated by further use of genetic and molecular biological face for phagocytosis. Drosophila CRQ is a CD36-like
approaches. receptor expressed on the cell surface of macrophages;
A variety of factors contributing to engulfment have genetic analyses have shown that it is required for phago-
been reported in nematodes, flies and mammals. Some cytosis of apoptotic corpses. Apoptosis is also accompa-
of the responsible factors, including CED-1, CED-2, nied by the exposure of phosphatidylserine on the outer
CED-5, CED-6, CED-7, CED-10, and CED-12 in C. cell surface of plasma membranes. Phosphatidylserine has
elegans, Croquemort (CRQ) in Drosophila melanogaster, also been regarded as a target molecule for phagocytosis;
and a phosphatidylserine receptor in mammals have re- the phosphatidylserine receptor has been cloned by phage
cently been identified. The CED-6 protein contains a display technique. It is expressed on various cells includ-
phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain at its N terminus ing macrophages, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells, and is
and putative Src-homology domain 3 (SH3)-binding sites. found in databases of Drosophila melanogaster and C. el-
It has been shown that this protein restores the function egans as a protein of unknown function. An antagonistic
of the clearance of apoptotic cells in engulfment-defective antibody against the phosphatidylserine receptor blocks
ced-6 mutants from C. elegans. The CED-7 protein is ho- engulfment of dying B and T cells by phagocytes, indi-
mologous to ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporters, is cating that this receptor is essential for phagocytosis of
FIGURE 6 Model for apoptotic chromosomal DNA degradation in vivo.