Page 12 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Molecular Biology
P. 12
P1: GQQ Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-90 May 17, 2001 20:42
550 Cell Death (Apoptosis)
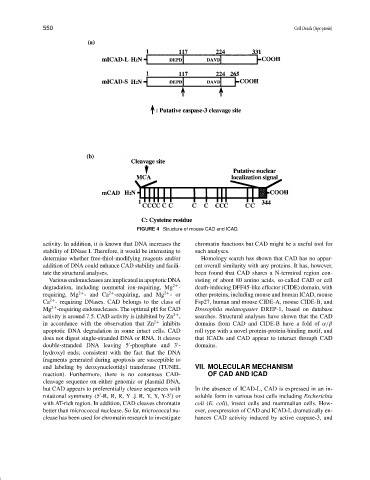
FIGURE 4 Structure of mouse CAD and ICAD.
activity. In addition, it is known that DNA increases the chromatin functions but CAD might be a useful tool for
stability of DNase I. Therefore, it would be interesting to such analyses.
determine whether free-thiol-modifying reagents and/or Homology search has shown that CAD has no appar-
addition of DNA could enhance CAD stability and facili- ent overall similarity with any proteins. It has, however,
tate the structural analyses. been found that CAD shares a N-terminal region con-
VariousendonucleasesareimplicatedinapoptoticDNA sisting of about 80 amino acids, so-called CAD or cell
2+
degradation, including nonmetal ion-requiring, Mg - death-inducing DFF45-like effector (CIDE) domain, with
2+
2+
2+
requiring, Mg - and Ca -requiring, and Mg -or other proteins, including mouse and human ICAD, mouse
Ca - requiring DNases. CAD belongs to the class of Fsp27, human and mouse CIDE-A, mouse CIDE-B, and
2+
Mg -requiring endonucleases. The optimal pH for CAD Drosophila melanogaster DREP-1, based on database
2+
activity is around 7.5. CAD activity is inhibited by Zn , searches. Structural analyses have shown that the CAD
2+
in accordance with the observation that Zn 2+ inhibits domains from CAD and CIDE-B have a fold of α/β
apoptotic DNA degradation in some intact cells. CAD roll type with a novel protein-protein-binding motif, and
does not digest single-stranded DNA or RNA. It cleaves that ICADs and CAD appear to interact through CAD
double-stranded DNA leaving 5 -phosphate and 3 - domains.
hydroxyl ends; consistent with the fact that the DNA
fragments generated during apoptosis are susceptible to
end labeling by deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TUNEL VII. MOLECULAR MECHANISM
reaction). Furthermore, there is no consensus CAD- OF CAD AND ICAD
cleavage sequence on either genomic or plasmid DNA,
but CAD appears to preferentially cleave sequences with In the absence of ICAD-L, CAD is expressed in an in-
rotational symmetry (5 -R, R, R, Y ⇓ R, Y, Y, Y-3 )or soluble form in various host cells including Escherichia
with AT-rich region. In addition, CAD cleaves chromatin coli (E. coli), insect cells and mammalian cells. How-
better than micrococcal nuclease. So far, micrococcal nu- ever, coexpression of CAD and ICAD-L dramatically en-
clease has been used for chromatin research to investigate hances CAD activity induced by active caspase-3, and