Page 79 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Molecular Biology
P. 79
P1: GSS/GLE P2: GPJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007I-331 July 3, 2001 18:42
690 Immunology—Autoimmunity
antigen, it has been found that autoantigens often com- acid components. This is usually achieved by metabolic
prise complexes of proteins and nucleic acids, such as the labeling of rapidly dividing cell clutures with a radioac-
32
35
snRNPs of the spliceosome. Precipitation of such macro- tive precursor such as [ S]methionine for proteins or Pi
molecular complexes is also the major disadvantage of for nucleic acids. The immunoprecipitated antigen is sub-
immunoprecipitation as it does not allow identification of jected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to resolve the
individual antigenic components. This drawback can be components and autoradiography to visualize the radiola-
overcome by using individual components in immuno- beled components.
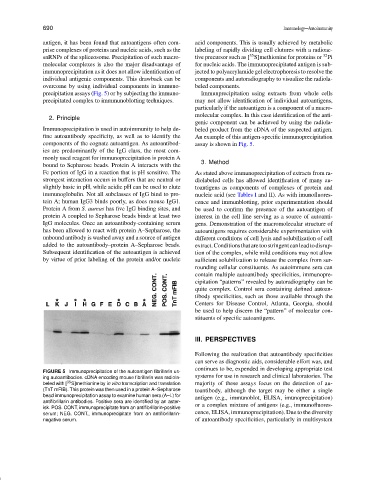
precipitation assays (Fig. 5) or by subjecting the immuno- Immunprecipitation using extracts from whole cells
precipitated complex to immmunoblotting techniques. may not allow identification of individual autoantigens,
particularly if the autoantigen is a component of a macro-
molecular complex. In this case identification of the anti-
2. Principle
genic component can be achieved by using the radiola-
Immunoprecipitation is used in autoimmunity to help de- beled product from the cDNA of the suspected antigen.
fine autoantibody specificity, as well as to identify the An example of this antigen-specific immunoprecipitation
components of the cognate autoantigen. As autoantibod- assay is shown in Fig. 5.
ies are predominantly of the IgG class, the most com-
monly used reagent for immunoprecipitation is protein A
3. Method
bound to Sepharose beads. Protein A interacts with the
Fc portion of IgG in a reaction that is pH sensitive. The As stated above immunoprecipitation of extracts from ra-
strongest interaction occurs in buffers that are neutral or diolabeled cells has allowed identification of many au-
slightly basic in pH, while acidic pH can be used to elute toantigens as components of complexes of protein and
immunoglobulin. Not all subclasses of IgG bind to pro- nucleic acid (see Tables I and II). As with imunofluores-
tein A; human IgG3 binds poorly, as does mouse IgG1. cence and immunblotting, prior experimentation should
Protein A from S. aureus has five IgG binding sites, and be used to confirm the presence of the autoantigen of
protein A coupled to Sepharose beads binds at least two interest in the cell line serving as a source of autoanti-
IgG molecules. Once an autoantibody-containing serum gens. Demonstration of the macromolecular structure of
has been allowed to react with protein A–Sepharose, the autoantigens requires considerable experimentation with
unbound antibody is washed away and a source of antigen different conditions of cell lysis and solubilization of cell
added to the autoantibody–protein A–Sepharose beads. extract.Conditionsthataretoostringentcanleadtodisrup-
Subsequent identification of the autoantigen is achieved tion of the complex, while mild conditions may not allow
by virtue of prior labeling of the protein and/or nucleic sufficient solubilization to release the complex from sur-
rounding cellular constituents. As autoimmune sera can
contain multiple autoantibody specificities, immunopre-
cipitation “patterns” revealed by autoradiography can be
quite complex. Control sera containing defined autoan-
tibody specificities, such as those available through the
Centers for Disease Control, Atlanta, Georgia, should
be used to help discern the “pattern” of molecular con-
stituents of specific autoantigens.
III. PERSPECTIVES
Following the realization that autoantibody specificities
can serve as diagnostic aids, considerable effort was, and
continues to be, expended in developing appropriate test
FIGURE 5 Immunoprecipitation of the autoantigen fibrillarin us-
systems for use in research and clinical laboratories. The
ing autoantibodies. cDNA encoding mouse fibrillarin was radiola-
35
beled with [ S]methionine by in vitro transcription and translation majority of these assays focus on the detection of au-
(TnT mFIB). This protein was then used in a protein A–Sepharose toantibody, although the target may be either a single
bead immunoprecipitation assay to examine human sera (A–L) for antigen (e.g., immunoblot, ELISA, imunoprecipitation)
antifibrillarin antibodies. Positive sera are identified by an aster-
isk. POS. CONT, immunoprecipitate from an antifibrillarin-positive or a complex mixture of antigens (e.g., immunofluores-
serum; NEG. CONT., immunoprecipitate from an antifibrillarin- cence, ELISA, immunoprecipitation). Due to the diversity
negative serum. of autoantibody specificities, particularly in multisystem