Page 156 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 156
136 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
there, but these are more initial and have maintenance cost. Research
is going on to increase the enzyme activity and reduce the initial cost.
i. Anaerobic Digestion (AD): The waste materials have a high- organic
content at the range of up to 40,000 mg/L total organic carbons. The
pH values vary low to high range from 2 to 12, and salt range is 5%;
some times more than that and so has maximum possible chance of the
presence of heavy metals and dangerous organics [26–28]. Aerobic or
anaerobic digestion is a process by which an organic matter is broken
down by microorganisms in the lack of oxygen, producing biogas, a
methane-rich gas used as a fuel, dig estate, and a source of nutrients
used as fertilizer. The period of operation per succession is usually from
15 to 30 days. The biogas naturally created in sealed tanks is utilized to
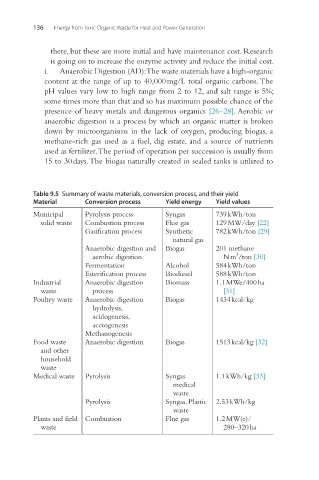
Table 9.5 Summary of waste materials, conversion process, and their yield
Material Conversion process Yield energy Yield values
Municipal Pyrolysis process Syngas 739 kWh/ton
solid waste Combustion process Flue gas 129 MW/day [22]
Gasification process Synthetic 782 kWh/ton [29]
natural gas
Anaerobic digestion and Biogas 201 methane
3
aerobic digestion N m /ton [30]
Fermentation Alcohol 584 kWh/ton
Esterification process Biodiesel 588 kWh/ton
Industrial Anaerobic digestion Biomass 1.1 MWe/400 ha
waste process [31]
Poultry waste Anaerobic digestion Biogas 1434 kcal/kg
hydrolysis,
acidogenesis,
acetogenesis
Methanogenesis
Food waste Anaerobic digestion Biogas 1513 kcal/kg [32]
and other
household
waste
Medical waste Pyrolysis Syngas 1.1 kWh/kg [33]
medical
waste
Pyrolysis Syngas. Plastic 2.53 kWh/kg
waste
Plants and field Combustion Flue gas 1.2 MW(e)/
waste 280–320 ha