Page 92 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 92
78 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
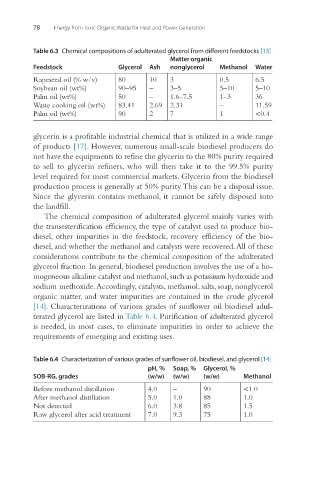
Table 6.3 Chemical compositions of adulterated glycerol from different feedstocks [13]
Matter organic
Feedstock Glycerol Ash nonglycerol Methanol Water
Rapeseed oil (% w/v) 80 10 3 0.5 6.5
Soybean oil (wt%) 90–95 – 3–5 5–10 5–10
Palm oil (wt%) 50 – 1.6–7.5 1–3 36
Waste cooking oil (wt%) 83.41 2.69 2.31 – 11.59
Palm oil (wt%) 90 2 7 1 <0.4
glycerin is a profitable industrial chemical that is utilized in a wide range
of products [17]. However, numerous small-scale biodiesel producers do
not have the equipments to refine the glycerin to the 80% purity required
to sell to glycerin refiners, who will then take it to the 99.5% purity
level required for most commercial markets. Glycerin from the biodiesel
production process is generally at 50% purity. This can be a disposal issue.
Since the glycerin contains methanol, it cannot be safely disposed into
the landfill.
The chemical composition of adulterated glycerol mainly varies with
the transesterification efficiency, the type of catalyst used to produce bio-
diesel, other impurities in the feedstock, recovery efficiency of the bio-
diesel, and whether the methanol and catalysts were recovered. All of these
considerations contribute to the chemical composition of the adulterated
glycerol fraction. In general, biodiesel production involves the use of a ho-
mogeneous alkaline catalyst and methanol, such as potassium hydroxide and
sodium methoxide. Accordingly, catalysts, methanol, salts, soap, nonglycerol
organic matter, and water impurities are contained in the crude glycerol
[14]. Characterizations of various grades of sunflower oil biodiesel adul-
terated glycerol are listed in Table 6.4. Purification of adulterated glycerol
is needed, in most cases, to eliminate impurities in order to achieve the
requirements of emerging and existing uses.
Table 6.4 Characterization of various grades of sunflower oil, biodiesel, and glycerol [14]
pH, % Soap, % Glycerol, %
SOB-RG, grades (w/w) (w/w) (w/w) Methanol
Before methanol distillation 4.0 – 90 <1.0
After methanol distillation 5.0 1.0 88 1.0
Not detected 6.0 3.8 85 1.5
Raw glycerol after acid treatment 7.0 9.3 75 1.0